Fedora 22 has been released on May 26, 2015 and we have been following it since the time it was made available. We have written a list of article on Fedora 22 which you may like to read.
- Fedora 22 Released – What’ New
- Fedora 22 Server Installation Guide
- Fedora 22 Workstation Installation Guide
The Fedora Fans would have already installed/updated Fedora 22 Workstation. If not, you will be doing to sooner or later. What after installation of Fedora 22? You would be eager to test your Fedora 22.
Here is the article where we will tell you about 13 useful things you should do immediately after Fedora 22 Workstation Installation.

1. Update Fedora 22 Distribution
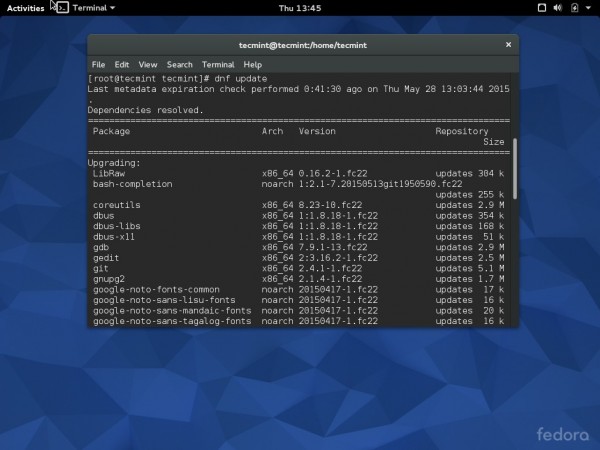
Though you have just installed/updated latest Fedora (version 22), you can not deny the fact that Fedora is a bleeding edge and when you try updating all the system packages even after installing the latest fedora build you may see a lots of applications and utility needs to be updated.
To update Fedora 22, we use DNF (a new package manager for Fedora) command as shown below.
# dnf update
2. Set Hostname in Fedora 22
We will not go into details of what is Host Name is and for what it is used. You would already be knowing much about this. If not, you may try goggling a bit. To set Host Name in Fedora 22, you may carry out the below operations.
First make sure to check your current hostname if any.
$ echo $HOSTNAME tecmint
Now change Hostname as:
# hostnamectl set-hostname - -static “myhostname”
Important: It is necessary to reboot your system for the changes to be taken into effect. After reboot you may check the host name similarly as we did above.
3. Set Static IP Address in Fedora 22
You would like to set static IP and DNS for your Fedora 22 Install. Static IP and DNS can be set in Fedora 22 as:
Edit the file /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 using your favorite editor or you may use default editor vim.
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
Important: Be aware that in your case eth0 might be replaced by enp0s3 or some other name. So, must verify it before changing anything….
Your ifcfg-eth0 file will look something like this.
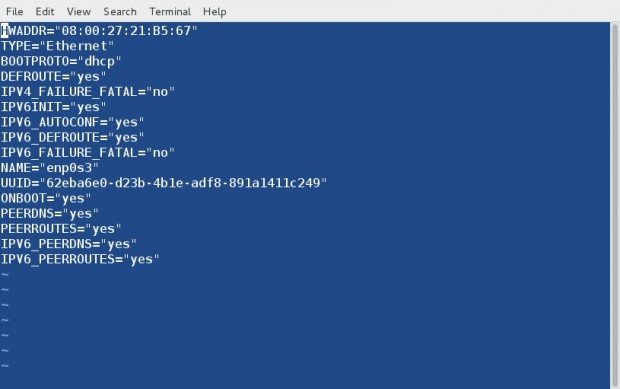
Now open and edit few things. Note you should enter ‘IPADDR’, ‘NETMASK’, ‘GATEWAY’, ‘DNS1’ and ‘DNS2’ as per your ISP.
BOOTPROTO="static" ONBOOT="yes" IPADDR=192.168.0.19 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.0.1 DNS1=202.88.131.90 DNS2=202.88.131.89
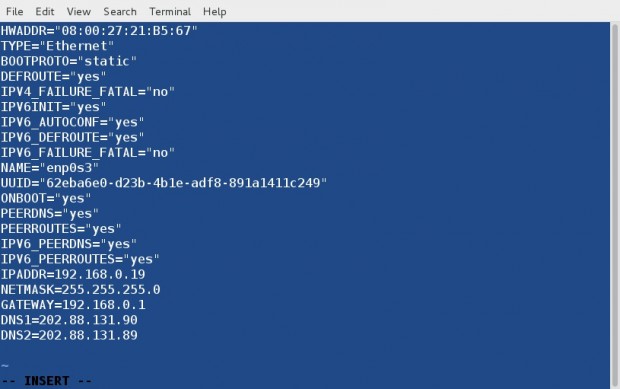
and finally save and exit. You need to restart the network service.
# systemctl restart network
After network restart you can verify your network details by issuing following command.
# ifconfig

4. Install Gnome Tweak Tool
Gnome Tweak Tool is an utility which lets you tweak and alter the default settings of Gnome Desktop Environment with ease. You can easily customize your Fedora workstation in GUI using Gnome Tweak Tool. Most of the options in Gnome Tweak Tool are self explanatory.
To install Gnome Tweak Tool:
# dnf install gnome-tweak-tool
Once installed, you can fire Gnome Tweak Tool from system Menu and commit the changes you want.
5. Enable Google Yum Repository
Google Provide various packages which can be installed directly from the repo. Packages like Google Chrome, Google Earth, Google Music Manager, Google Voice and Video Chat, mod_pagespeed for Apache and Google Web Designer can be installed right from the command Line without any extra work.
To add Google Repository run all the below command in your Linux Console, as root.
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/google-chrome.repo
Add following lines:
[google-chrome] name=google-chrome - $basearch baseurl=http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/rpm/stable/$basearch enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://dl-ssl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub
6. Install Google Chrome Browser
Although Mozilla Firefox is installed in Fedora 22 workstation by default, and I must admit it is one of the best browser available today with most number of plugins, however when it comes to speed nothing beats Google Chrome.
Install Google Chrome Stable as:
# dnf install google-chrome-stable
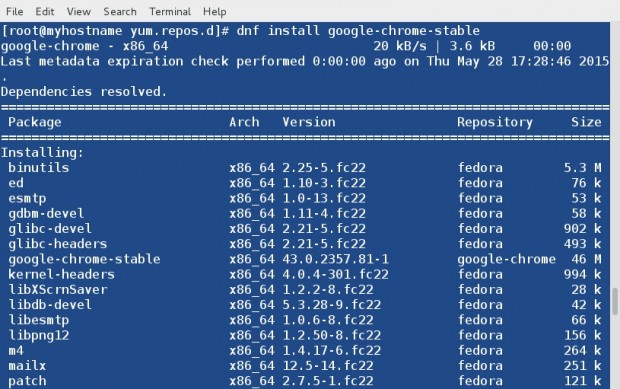
After Google Chrome has been installed, you can start it by going to Application Menu.

7. Install Fedy Tool
Fedy tool is must for those who want to run all those desktop applications for better user experience and day to day use by a normal desktop users.
You can install a variety of Applications that are very widely used by desktop users viz., Abobe Flash, Android Studio, Atom Text Editor, Dropbox for Nautilus, Gnome Development Tools, Master PDF Editor, Multimedia Codecs, Oracle JDK & JRE, Popcorn Time, Skype, Steam – for gaming, TeamViewer, Viber and etc,..
To install fedy run the following commands.
# dnf update # curl http://folkswithhats.org/fedy-installer -o fedy-installer && chmod +x fedy-installer && ./fedy-installer
Fire Fedy from Application Menu.

For details on how to use Fedy tool you may like to go through this Tweak Fedora Systems Using Fedy.
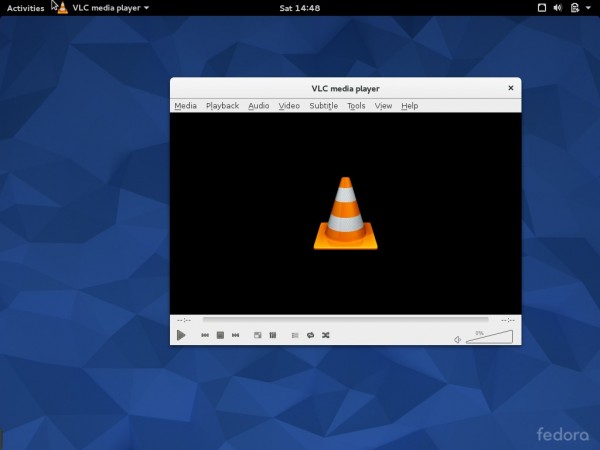
8. Install VLC on Fedora 22
VLC is a media player for almost all video formats. No matter what platform and system you are on, vlc is among those programs that will be there in program menu always. When you installed fedy tool (above), it automatically added and enabled RPMFUSION repository to install vlc under Fedora 22 System.
# dnf install vlc
9. Install Docky on Fedora 22
Docky is a doc bar inspired by doc in Mac. It holds all those frequently used application shortcuts for you that are most frequently used. You can configure it to hold shortcuts of required programs. It is a very light application and is very low on memory.
Install docky as:
# dnf install docky
After install, fire it from the application menu (Preferred) or right from the terminal. You may set it to install right at the boot from the docky settings.
10. Install Unrar and 7zip
Unrar is an utility that extract rar archives. Where as 7zip is an utility that extract archives of all types.
You may install both these utilities as:
# dnf install unrar p7zip
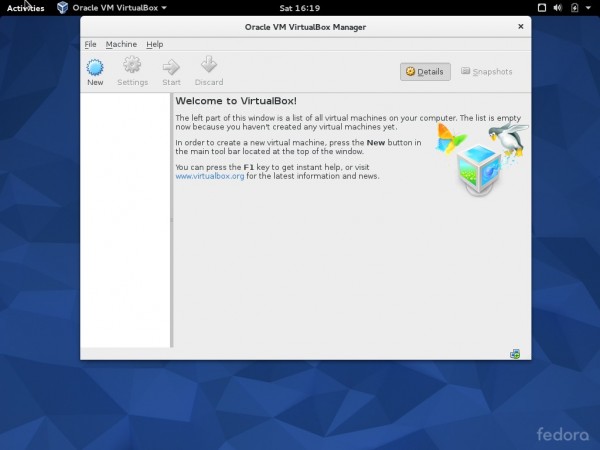
11. Install VirtualBox on Fedora 22
If you are on a Linux System, means you are very different than Users on other platforms like windows. You probably need to test and deploy a lots of products and applications and hence you need a virtual machine.
Virtualbox is one of the most widely used virtualization tool. Although Boxes – Virtualization tool is already available by default on Fedora 22 Install, still nothing beats the easiness of Virtualbox.
Although I have not used boxes yet myself and I am not sure what features it have, still I am addicted to virtualbox and it will take some time to switch to other virtualization tool.
To install Virtualbox, you need to download and enable virtualbox repository as:
# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/ # wget http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/rpm/fedora/virtualbox.repo
Update repolist.
# dnf -y update
Install Prerequisite and Virttualbox.
# dnf install -y kernel-headers kernel-devel dkms gcc # dnf -y install VirtualBox-4.3 # /etc/init.d/vboxdrv setup
Create an User for Virtualbox as:
# usermod -G vboxusers -a user_name # passwd user_name
To start Virtualbox you may need to run.
# /etc/init.d/vboxdrv start
Virtualbox UI can then be started from the Application Menu.
12. Install Various Desktop Environments
If you are interested in other Desktop Environment other than Gnome, you may install them as:
# dnf install @kde-desktop [KDE Desktop] # dnf install @xfce-desktop [XFCE Desktop] # dnf install @mate-desktop [Mate Desktop]
Note: You can Install any other desktop environment as:
# dnf install @DESKTOP_ENVIRONMENT-desktop
13. Learn DNF – Package Manager
You are aware of the fact that YUM is deprecated and DNF has replaced it.
To manage a system efficiently, you must have a good command over package Manager. Here is the list of 27 most frequently used DNF commands, you should master to yield most out of your system that too efficiently.
That’s all for now. The above said 13 points are enough to make most out of your Fedora 22 Workstation. You may like to add your point of view, if any through the comments box below. Stay tuned and connected to Tecmint. Enjoy!