Apache Tomcat (earlier known as Jakarta Tomcat) is an open-source web server developed by Apache Foundation to provide a pure Java HTTP server, which will enable you to run Java files easily, which means that Tomcat is not a normal server like Apache or Nginx, because its main goal is to provide a good web environment to run Java applications only unlike other normal web servers.
This article will walk you throughout the installation of Apache Tomcat 9 on RHEL/CentOS 8/7/6.
For Ubuntu, follow How to Install Apache Tomcat in Ubuntu.
Step 1: Installing and Configuring Java
Before heading up for the Tomcat installation, make sure you must have JAVA installed on your Linux box to run Tomcat. If not, install the latest version of JAVA or use the following yum command to install available Java from the default repositories.
# yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel #install JDK 8 OR # yum install java-11-openjdk-devel #install JDK 11
Once Java installed, you can verify the newly installed JAVA version running the following command on your system.
# java -version
Sample Output
openjdk version "11.0.4" 2019-07-16 LTS OpenJDK Runtime Environment 18.9 (build 11.0.4+11-LTS) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM 18.9 (build 11.0.4+11-LTS, mixed mode, sharing)
Step 2: Installing Apache Tomcat 9
After installing JAVA on the system, now it’s time to download the latest version of Apache Tomcat (i.e. 9.0.26) is the most recent stable version at the time of writing this article. If you want to make a cross-check, head over to following Apache download page and check if there is a newer version available.
Now download the latest version of Apache Tomcat 9, using following wget command and set up it as shown.
# cd /usr/local # wget https://mirrors.estointernet.in/apache/tomcat/tomcat-9/v9.0.37/bin/apache-tomcat-9.0.37.tar.gz # tar -xvf apache-tomcat-9.0.37.tar.gz # mv apache-tomcat-9.0.37.tar.gz tomcat9
Note: Replace the version number above with the latest version available if it was different.
Before starting the Tomcat Service, configure a CATALINA_HOME environment variable in your system using the following command.
# echo "export CATALINA_HOME="/usr/local/tomcat9"" >> ~/.bashrc # source ~/.bashrc
Now we all set to start the tomcat web server using the scripts provided by the tomcat package.
# cd /usr/local/tomcat9/bin # ./startup.sh
Sample Output
Using CATALINA_BASE: /usr/local/tomcat9 Using CATALINA_HOME: /usr/local/tomcat9 Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /usr/local/tomcat9/temp Using JRE_HOME: /usr Using CLASSPATH: /usr/local/tomcat9/bin/bootstrap.jar:/usr/local/tomcat9/bin/tomcat-juli.jar Tomcat started.
Now to open Tomcat from your browser, go to your IP or domain with the 8080 port (because Tomcat will always run on the 8080 port) as an example: mydomain.com:8080, replace mydomain.com with your IP or domain.
http://Your-IP-Address:8080 OR http://Your-Domain.com:8080
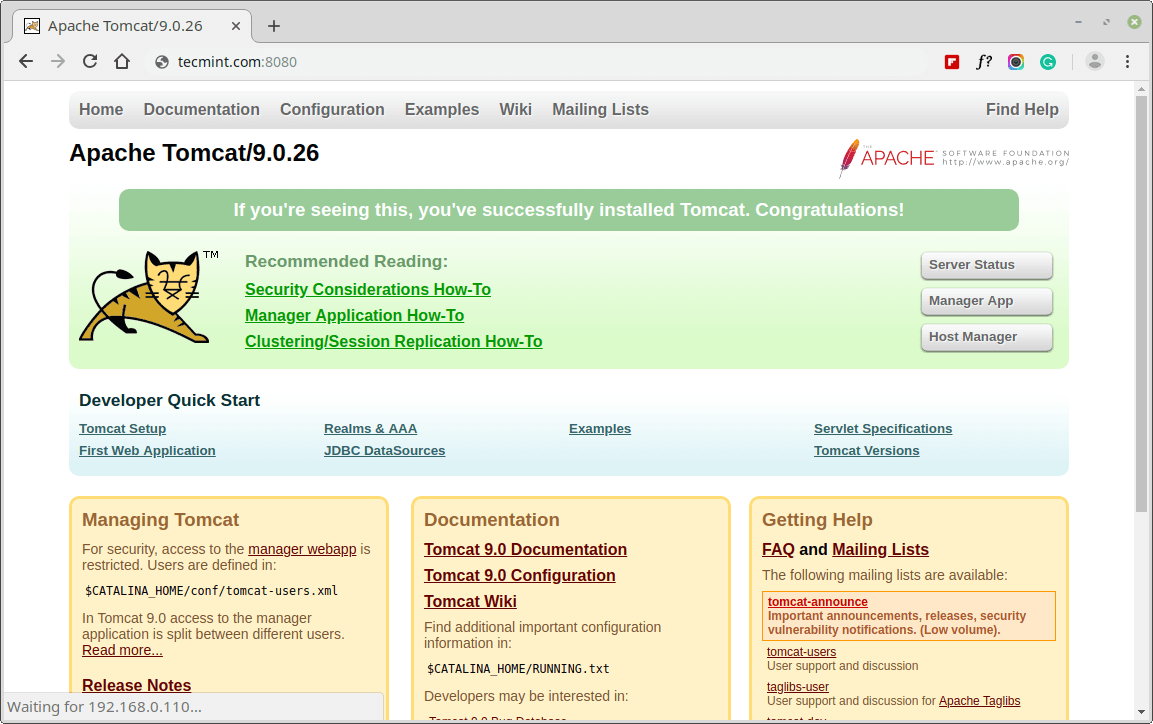
The default directory for Tomcat files will be in /usr/local/tomcat9, you can view the configuration files inside the conf folder, the main page that you have seen above, when you open your website on the 8080 port is in /usr/local/tomcat9/webapps/ROOT/.
Step 3: Configuring Apache Tomcat 9
By default you only able to access the default Tomcat page, to access admin and other sections like Server Status, Manager App and Host Manager. You need to configure user accounts for admins and managers.
To do so, you need to edit the ‘tomcat-users.xml‘ file located under /usr/local/tomcat9/conf directory.
Setup Tomcat User Accounts
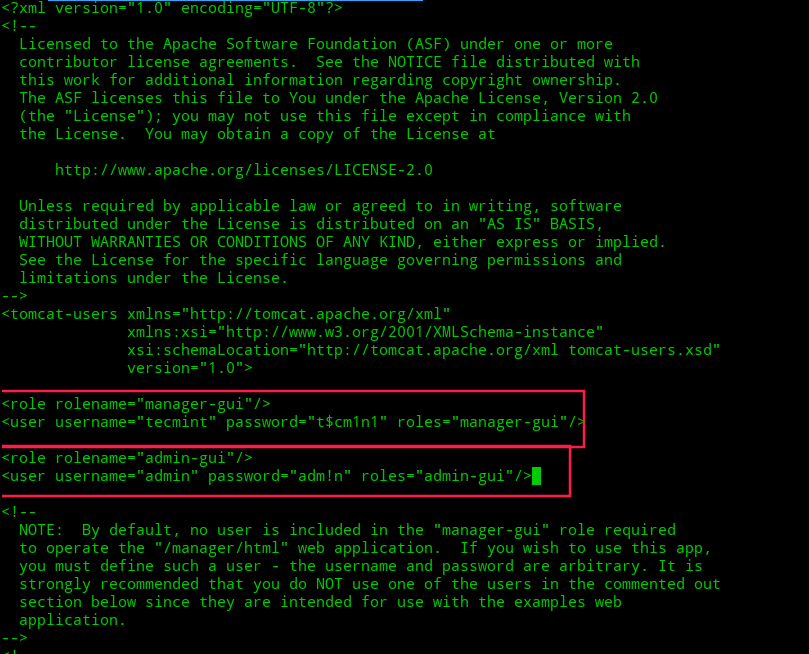
For example, to assign the manager-gui role to a user named ‘tecmint‘ with a password ‘t$cm1n1‘, add the following line of code to the config file inside the section.
# vi /usr/local/tomcat9/conf/tomcat-users.xml
<role rolename="manager-gui"/> <user username="tecmint" password="t$cm1n1" roles="manager-gui"/>
Similarly, you can also add an ‘admin-gui‘ role to an admin user named ‘admin‘ with a password ‘adm!n‘ as shown below.
<role rolename="admin-gui"/> <user username="admin" password="adm!n" roles="admin-gui"/>
Enable Remote Access to Tomcat
By default, access to the Manager and Host Manager section is restricted to the localhost only, to allow access to these pages, you need to mention IP address or network range in a configuration file.
# vi /usr/local/tomcat9/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml
Then look for the following line and change it to this to allow tomcat access from IP address 192.168.56.10.
allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::1|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 |192.168.56.10" />
You can also allow tomcat access from the local network 192.168.56.0.
allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::1|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 |192.168.56.*" /gt;
After setting up the admin and manager’s roles, restart the Tomcat and then try to access the admin section.
./shutdown.sh ./startup.sh
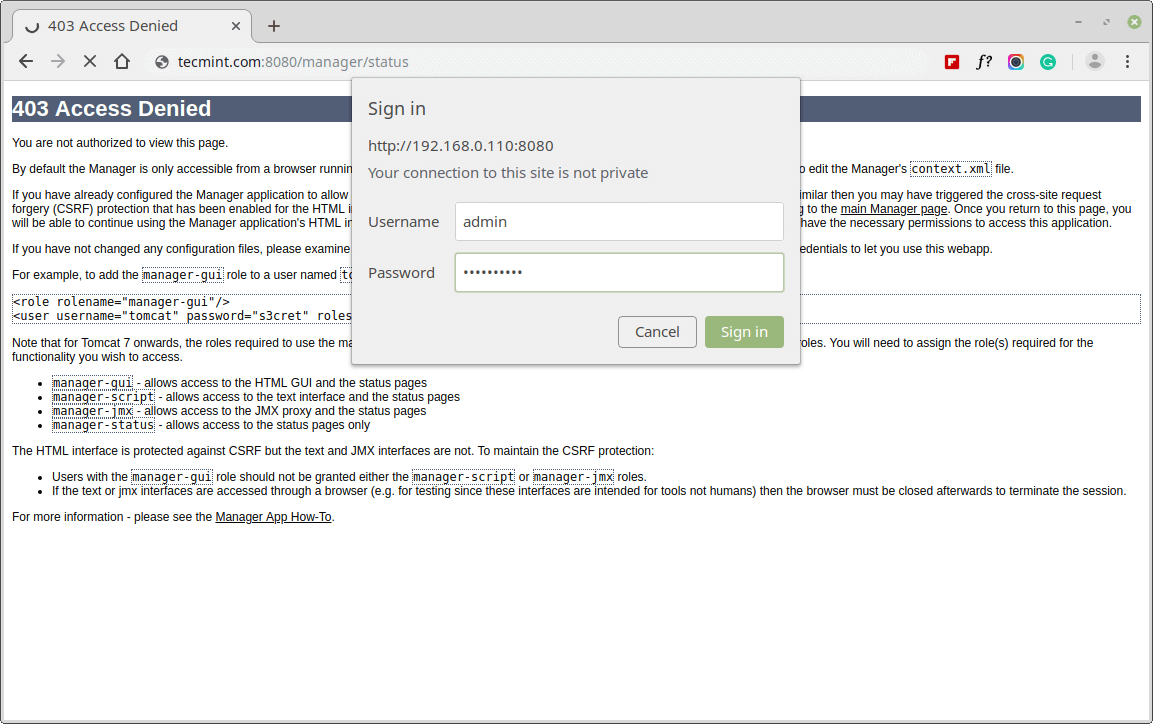
Now click on the ‘Server Status‘ tab, it will prompt you to enter user credentials, enter username and password that you’ve added above in the config file.
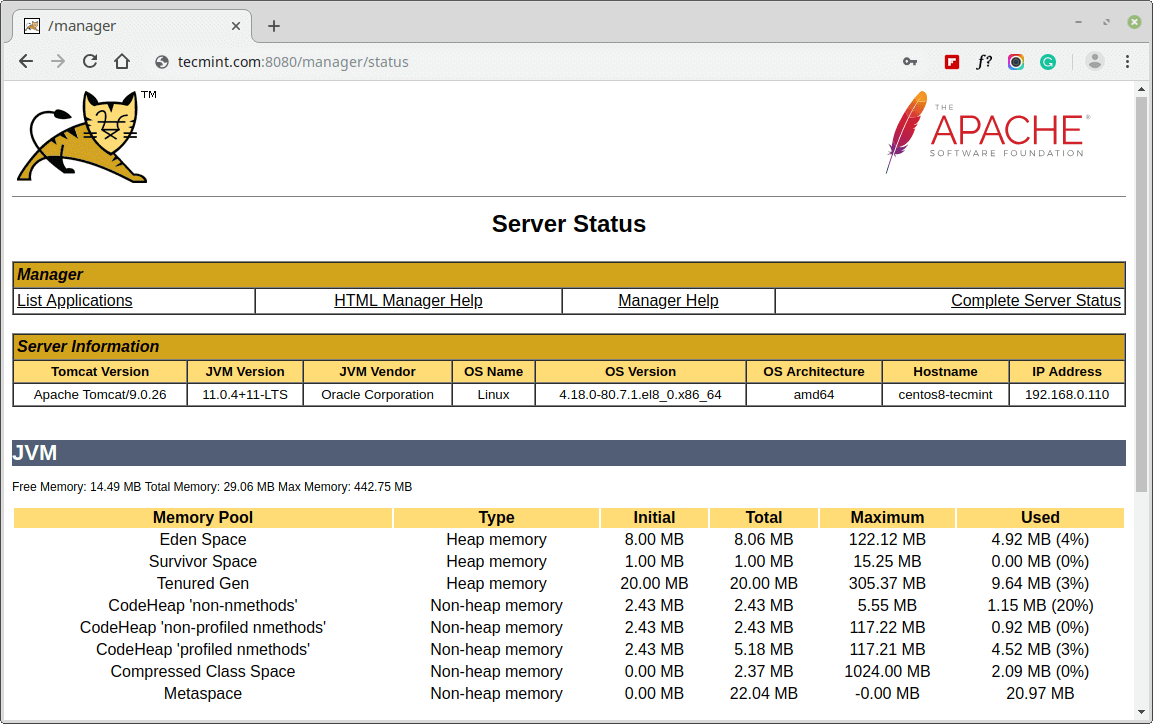
Once, you enter user credentials, you will find a page similar to below.
Changing Apache Tomcat Port
If you want to run Tomcat on different port say 80 port. You will have to edit the ‘server.xml‘ file in ‘/usr/local/tomcat9/conf/‘. Before changing, port, make sure to stop the Tomcat server using.
# /usr/local/tomcat9/bin/shutdown.sh
Now open the server.xml file using the Vi editor.
# vi /usr/local/tomcat9/conf/server.xml
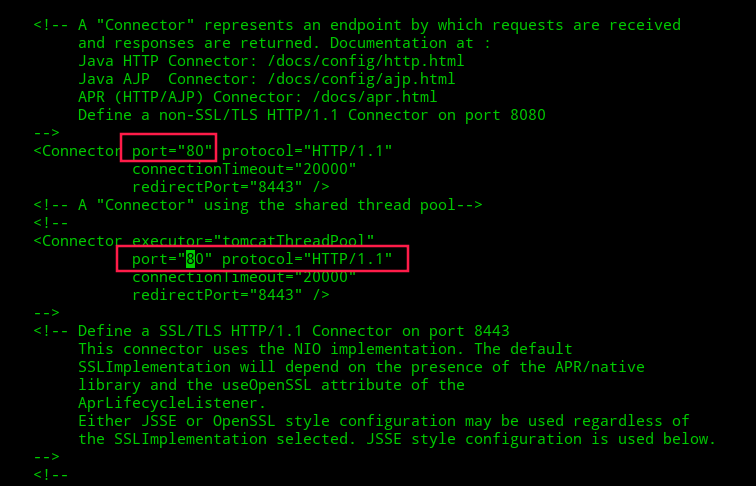
Now search for “Connector port” and change its value from 8080 to 80 or any other port you want as it follows.
To save the file and restart the Apache Tomcat server again, using the below command.
# /usr/local/tomcat9/bin/startup.sh
That’s it, your Tomcat server will be running on the 80 port.
Of course, you have to run all the above commands as a root, if you don’t they won’t work because we are working on the ‘/usr/local‘ directory which is a folder owned by the root user only if you want you can run the server as a normal user but you will have to use your HOME folder as a working area to download, extract and run the Apache Tomcat server.
To get some information about your running Tomcat server and your computer, run.
/usr/local/tomcat9/bin/version.sh
Sample Output
Using CATALINA_BASE: /usr/local/tomcat9 Using CATALINA_HOME: /usr/local/tomcat9 Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /usr/local/tomcat9/temp Using JRE_HOME: /usr Using CLASSPATH: /usr/local/tomcat9/bin/bootstrap.jar:/usr/local/tomcat9/bin/tomcat-juli.jar NOTE: Picked up JDK_JAVA_OPTIONS: --add-opens=java.base/java.lang=ALL-UNNAMED --add-opens=java.base/java.io=ALL-UNNAMED --add-opens=java.rmi/sun.rmi.transport=ALL-UNNAMED Server version: Apache Tomcat/9.0.26 Server built: Sep 16 2019 15:51:39 UTC Server number: 9.0.26.0 OS Name: Linux OS Version: 4.18.0-80.7.1.el8_0.x86_64 Architecture: amd64 JVM Version: 11.0.4+11-LTS JVM Vendor: Oracle Corporation
That’s it! Now you can start deploying JAVA based applications under Apache Tomcat 9. For more about how to deploy applications and create virtual hosts, check out the official Tomcat documentation.