Linux top command is highly used by system administrators to display system statistics in real time regarding system uptime and load average, used memory, running tasks, a summary of processes or threads and detailed information about each running process.
However, besides real time viewing of the running system, top command output can be saved to a file, by using the -b flag, which instructs top to operate in batch mode and -n flag to specify the amount of iteration the command should output.
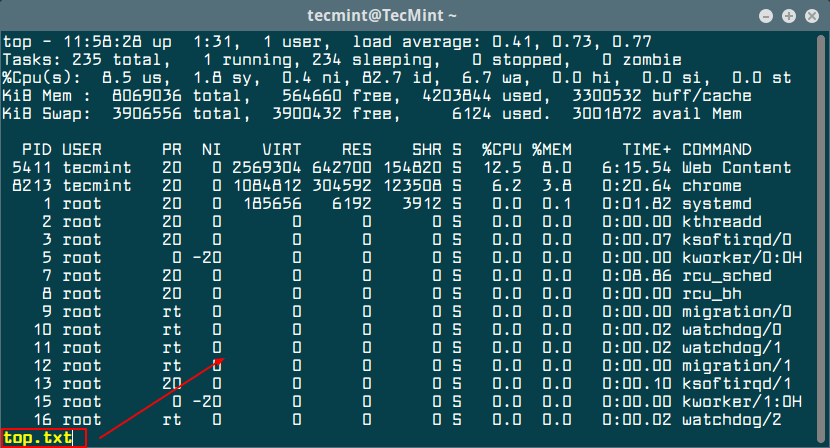
In the below example, we’ll redirect the output of top command to top.txt file in the current working directory. The -n argument will be used to send only one snapshot of the command to the mentioned file.
$ top -b -n 1 > top.txt
To read the resulted file, use a command line file reader utility, such as cat command, less or more.
$ less top.txt
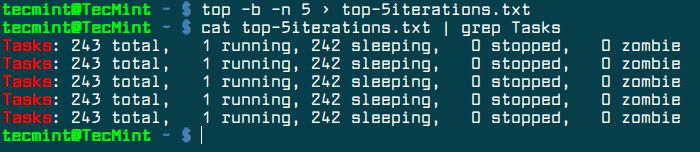
To grab five iteration of top command, execute the command as shown in the below excerpt.
$ top -b -n 5 > top-5iterations.txt
In order to display only the number of running tasks from the resulted file, use the grep filter, as shown in the below command example.
$ cat top-5iterations.txt | grep Tasks
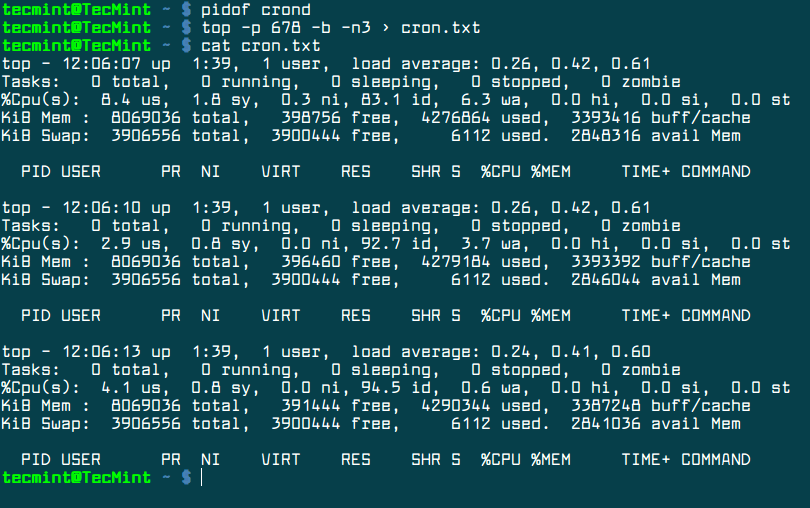
To take a snapshot of a specific process in top utility, execute command with the PID (-p) flag. To get the PID of a running process, issue pidof command against the name of the running process.
In this example we’ll monitor the cron process via top command by taking three snapshots of the PID.
$ pidof crond $ top -p 678 -b -n3 > cron.txt $ cat cron.txt
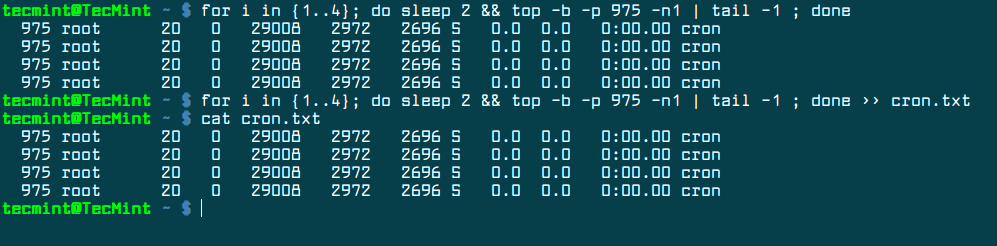
Using a for iteration loop, we can display a process statistics via its PID, each two seconds, as shown in the below example. The output of the loop can also be redirected to a file. We’ll use the same cron PID as shown in the above example.
$ for i in {1..4}; do sleep 2 && top -b -p 678 -n1 | tail -1 ; done
Redirect loop output to file.
$ for i in {1..4}; do sleep 2 && top -b -p 678 -n1 | tail -1 ; done >> cron.txt
$ cat cron.txt
These are just a few examples on how you can monitor and gather system and process statistics via top command.





Wonderful command saves my time.
for i in {1..4}; do sleep 2 && top -b -p 678 -n1 | tail -1 ; done >> cron.txt