If you are a Fedora fan, I’m sure that you know that Fedora 26 has been released and we are closely following it ever since, Fedora 26 came with many new changes that you can view in their official release announcement page.
In this guide, we will show you some useful tips on what to do after installing Fedora 26 Workstation to make it even better.
1. Update Fedora 26 Packages
Even though you might have just installed/upgraded Fedora, there will most probably be packages available for update. After all Fedora is the one to always use the latest releases of each software it has and package updates are released quite often.
To run the update, use the following command:
# dnf update
2. Set Hostname in Fedora 26
We will use hostnamectl command, which is used to query and set system hostname and related settings. This tool is used to manage three different hostnames classes and they are: static, pretty, and transient.
The static host name is the universal hostname, which can be selected by the system user, and is saved in the /etc/hostname file.
Here, we will not going to discuss much about pretty, and transient hostnames classes, our main motive is to set system hostname, so here we go…
First list the current hostname using the following command:
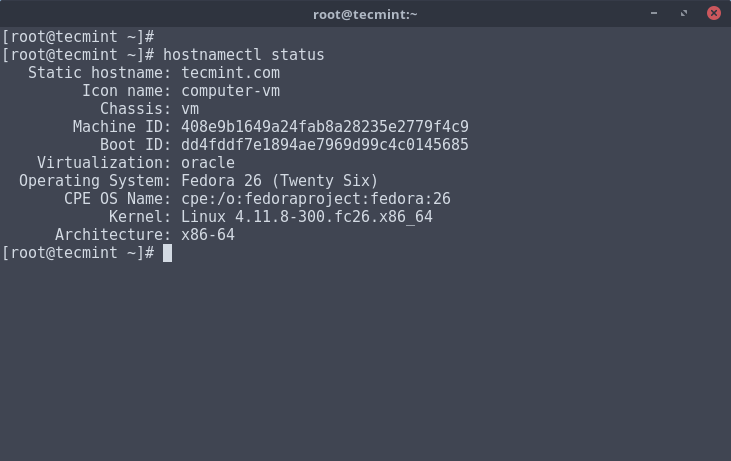
# hostnamectl status
Sample Output
Static hostname: localhost.localdomain
Icon name: computer-vm
Chassis: vm
Machine ID: 458842014b6c41f9b4aadcc8db4a2f4f
Boot ID: 7ac08b56d02a4cb4a5c5b3fdd30a12e0
Virtualization: oracle
Operating System: Fedora 26 (Twenty Six)
CPE OS Name: cpe:/o:fedoraproject:fedora:26
Kernel: Linux 4.11.8-300.fc26.x86_64
Architecture: x86-64
Now change Hostname as:
# hostnamectl set-hostname --static “tecmint.com”
Important: It is necessary to reboot your system for the changes to be taken into effect. After reboot, make sure to check the host name similarly as we did above.
3. Set Static IP Address in Fedora 26
To set system static IP address, you need to open and edit your network configuration file called enp0s3 or eth0 under /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ directory.
Open this file with the choice of your editor.
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3
Sample Output
HWADDR=08:00:27:33:01:2D TYPE=Ethernet BOOTPROTO=dhcp DEFROUTE=yes PEERDNS=yes PEERROUTES=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_PEERDNS=yes IPV6_PEERROUTES=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no NAME=enp0s3 UUID=1930cdde-4ff4-4543-baef-036e25d021ef ONBOOT=yes
Now make the changes as suggested below and save the file..
BOOTPROTO="static" ONBOOT="yes" IPADDR=192.168.0.102 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.0.1 DNS1=202.88.131.90 DNS2=202.88.131.89
Important: Make sure to replace network configuration in the above file with your own network settings.
After making above changes, make sure to restart the network service to take new changes into effect and verify the IP address and network settings with the help of following commands.
# service network restart # ifconfig

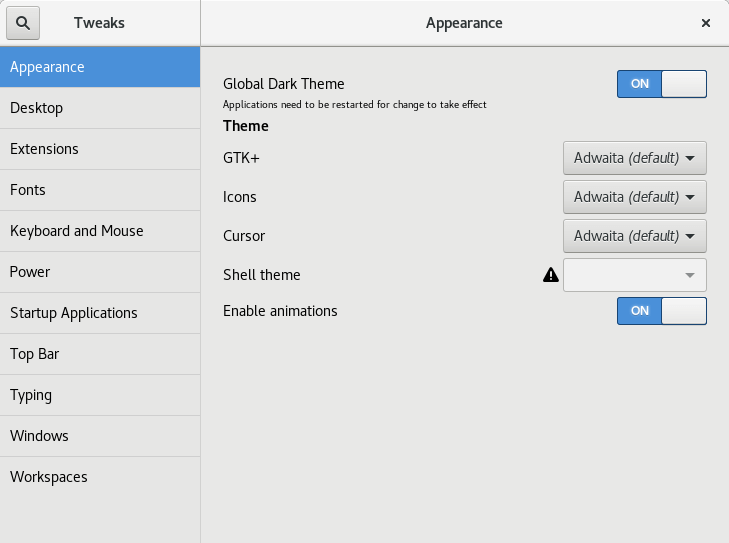
4. Install Gnome Tweak Tool
Fedora 26 uses Gnome 3.24 which is the latest version of the gnome-shell desktop environment. To change some of it’s settings, you can install the Gnome Tweak Tool.
This tool allows you to change the Gnome-shell settings like:
- Appearance
- Desktop decoration
- Easily install extensions
- Top bar
- Workspaces
- Windows
To install Gnome Tweak Tool click on “Activities” menu on the top left and search for “Software“. In the software manager, search for “Gnome Tweak Tool” and in the list of results click on the “Install” button or install from the commandline.
# dnf install gnome-tweak-tool
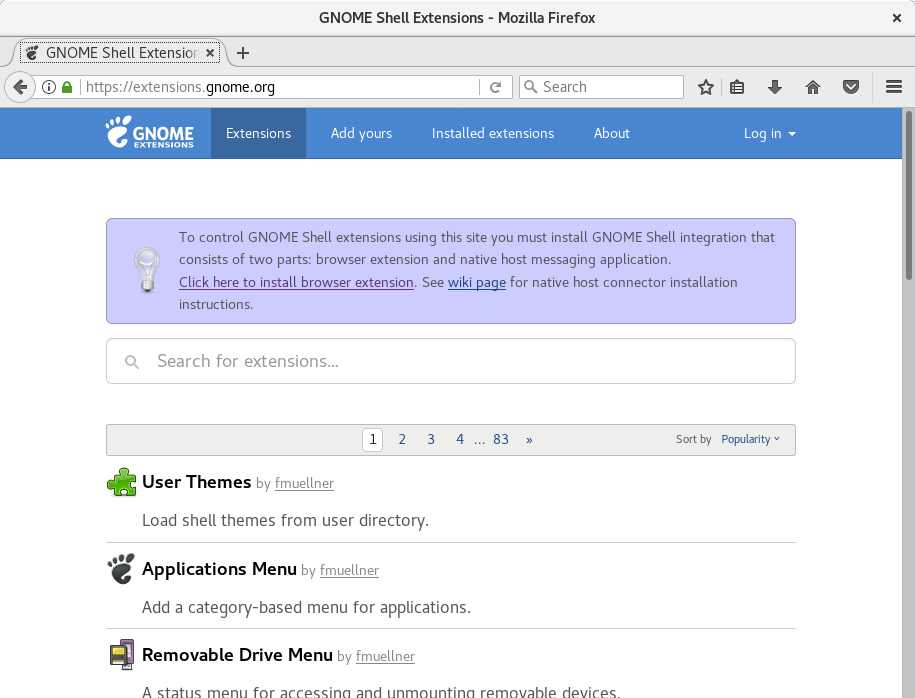
5. Install Gnome Shell extensions
The Gnome Shell desktop environment can be modified even further and you can tweak it to your needs, by installing Gnome Shell Extensions. This can be easily done from the official website for Gnome Shell Extensions at gnome.org:
Installation of new modules is simple. Simply open the page for the extension you wish to have installed and use the on/off switch to activate/deactivate a Gnome Shell extension on your system:
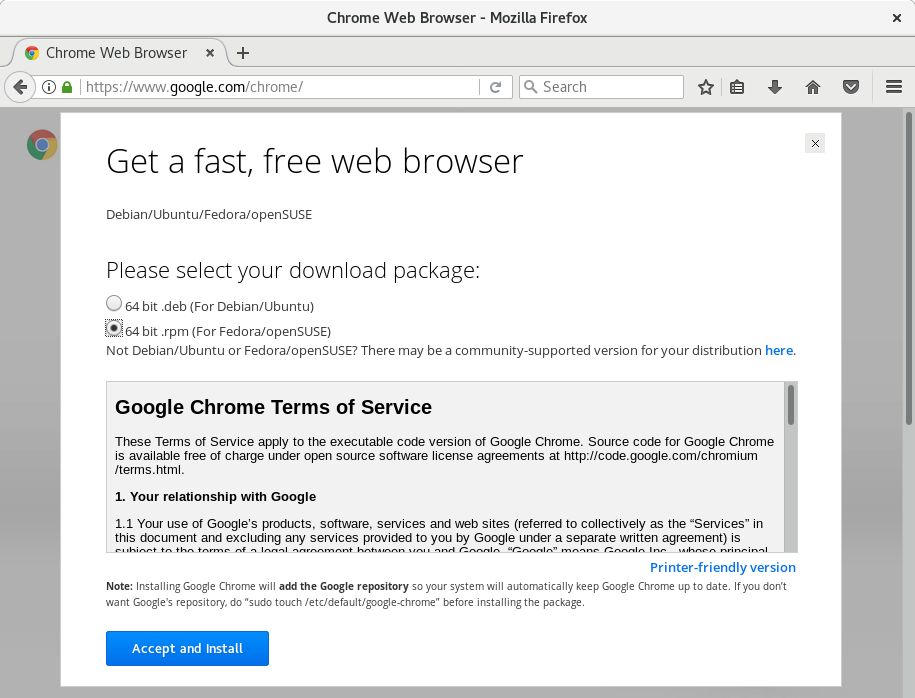
6. Install Google Chrome
Google Chrome is a web browser, developed by Google. It’s a lightweight, modern browser designed to improve browsing experience. You can also install Google Chrome extensions to make Chrome even better.
To download the latest version of Google Chrome go to:
From that page, download the “rpm” package that’s designed for your OS architecture (32/64 bit). Once the download is complete, double click the downloaded file and click “install” button to complete the installation.
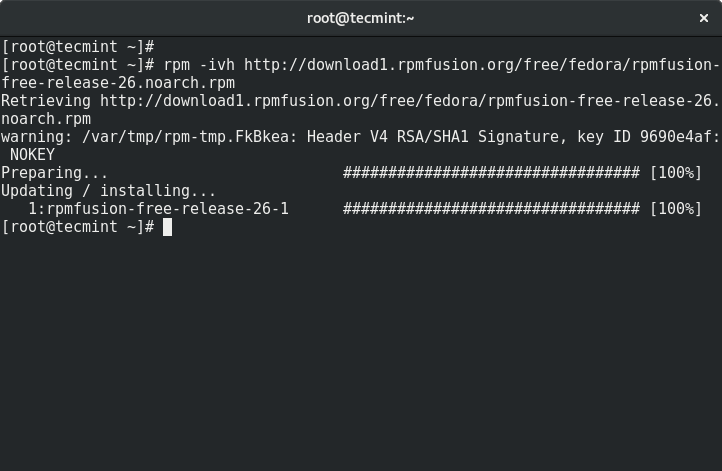
7. Activate RPMFusion repo
The RPMFusion provides some free and non-free software for Fedora. The repo can be used via the command line. The repository is meant to provide stable and tested packages for Fedora so it is highly recommended to activate it on your system with:
# rpm -ivh http://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-26.noarch.rpm
8. Install VLC Media Player
VLC is a multi-platform media player that supports nearly every video format available. It’s one of the best in it’s category and if you like watching movies or listening to music we encourage you to install it.
The VLC package is included in the RPMFusion repository that was enabled in point 7. To complete the installation of VLC open new terminal and submit the following command:
# dnf install vlc
9. Install DropBox
DropBox is a famous Cloud storage service that can be used on multiple platforms. It can be used to store or backup your files on the cloud and access them from everywhere.
You can install Dropbox on your PC, tablet or smartphone and have your files accessed. To install a DropBox desktop client in Fedora 26 go to Dropbox’s website and download the Fedora package in accordance to your OS architecture (32/64 bit):
When the download completes, find the downloaded file and click on “Install” button to complete the installation.
10. Install Mozilla Thunderbird
Fedora comes with pre-installed “Evolution” mail client. It’s good for reading mails, but if you need to have a more organized to read and keep your emails, Mozilla Thunderbird is the right choice for you.
To install Mozilla Thunderbird, open the Fedora software manager and search for “Thunderbird“. After that click the “Install” button next to the package.
11. Enable Google Repository
Google provides its own repository from where you can install Google software such as Google Earth, Google Music manager and others. To add Google’s repo to your Fedora installation, use the following commands:
# gedit /etc/yum.repos.d/google-chrome.repo
Now copy/paste the following code and save the file:
[google-chrome] name=google-chrome baseurl=http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/rpm/stable/$basearch enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://dl-ssl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub
12. Install Docky
Docky is a simple, attractive and productive dock used on many different Linux distribution. Docky doesn’t use much system resources and yet it improves your productivity while looking good on your screen. If you want to have a good looking dock such as Docky, use the following commands:
# dnf install docky
13. Install other Desktop Environments
If you are not big fan of Gnome shell, we have some good news for you. You can install different desktop environments on your Fedora workstation. To complete the install, you will need to run the commands below in a terminal. Only run the command that is related to the desktop environment that you wish to use:
Install Mate Desktop
# dnf install @mate-desktop
Install KDE Desktop
# dnf install @kde-desktop
Install XFCE Desktop
# dnf install @xfce-desktop
LXDE Desktop
# dnf install @lxde-desktop
Install Cinnamon Desktop
# dnf install @cinnamon-desktop
14. Install rar and zip utilities
Often we use archives in our daily routines. Extracting some of the archives require proper tools to be installed. To deal with .rar and .zip type of compressed files, you can install the required utilities with this command:
# dnf install unzip
15. Install Java Plugins for web
Java is a programming language which many websites use to display different type of data. To be able to load such type of websites, you will need the JAVA plugins for web. They can be easily installed by running the following command in a terminal:
# dnf install icedtea-web java-openjdk
16. Install GIMP
GIMP is a small, yet powerful image manipulation software. You can use GIMP to edit your images or in a paint like style. Either way this is a useful tool, that you will want in your collection of programs.
To install GIMP simply run:
# dnf install gimp
17. Install Pidgin
Pidgin is a chat client that supports multiple social accounts. You can use it to easily interact with your friends, family or co-workers. The installation of Pidgin in Fedora is fairly easy and can be completed with the following command:
# dnf install pidgin
18. Install qbittorrent
Torrent trackers are gaining more and more popularity in the last few years. Thanks to torrents, you can download important files with a very good speed as long as there are enough seeders.
To download such files, you will need a torrent client software. This is why we recommend qBittorrent. It’s an advanced torrent client with friendly interface.
You can install it by launching the “Software” manager from your Gnome dashboard. Within the software manager, search for “qbittorrent“. Once you have found the package, click the “Install” button next to that package:
Alternatively, you can install qbittorrent with the following command executed in a terminal:
# dnf install qbittorrent
Here is how the qBittorent interface looks like:
19. Install VirtualBox
Virtualbox is a software through which you can test different operating systems on your computer, without having to re-install your OS itself.
To install VirtualBox on your Fedora you must have the RPMFusion repository enabled (see point 7). Then you can install VirtualBox with the following command:
# dnf install VirtualBox
20. Install Steam
If you like playing games on your Fedora then Steam is for you! It has many different games included in it that can be ran on different platforms including Linux.
In a simple words it’s a game store where you can download games for your Fedora system and play them after that. To install Steam on your Fedora installation run the following commands:
# dnf config-manager --add-repo=http://negativo17.org/repos/fedora-steam.repo # dnf -y install steam
After that you can launch steam from the Gnome-shell dash.
Read Also: Best Linux Games of 2015
21. Install Spotify
I think you all know what Spotify is. It’s currently the best service for music streaming on all your devices. The official client for Spotify on Linux boxes is meant for Debian/Ubuntu derivatives.
The fedora package reassembles the Ubuntu package and moves all the files in the required places. So to install Spotify client on your Fedora installation, you will need to use the following commands:
# dnf config-manager --add-repo=http://negativo17.org/repos/fedora-spotify.repo # dnf install spotify-client
22. Install Wine
Wine is a software meant to help you run Windows applications under Linux. While not all applications may run is expected, this is a useful tool if you need to run a Windows program under Fedora.
To complete the install of Wine, run the following command in your terminal:
# dnf install wine
23. Install Youtube-DL
Youttube-DL is a python based tool that allows you to download videos from sites such as YouTube.com Dailymotion, Google Video, Photobucket, Facebook, Yahoo, Metacafe, Depositfiles.
If you are interested in such tool and like to have some videos for offline watching, then you can install this tool by running:
# dnf install youtube-dl
For complete guide how to use this tool, please check our guide:
24. Install Simple Scan
Simple scan enables to easily capture scanned documents, it is simple and easy to use as the name states. It is useful especially for those using Fedora 24 and Fedora 25 workstation in an small home office. You can find it in Software manager application.
# dnf install simple-scan
25. Install Fedora Media Writer
Fedora Media Writer is the default application provided by Fedora for creating live USB or bootable images. Unlike most image writers, Fedora Media Writer can download images (Fedora Workstation and Fedora Server), but it limited to Fedora only, but also can able to write ISO for any distributions.
# dnf install mediawriter
26. Install GNOME Music Player
GNOME music is a relatively new music player that offers some of the best music player features and functionalities, more importantly, it is simple and easy to use.
# dnf install gnome-music
27. Add Online Accounts
Fedora enables you to access your online accounts directly on the system, you add them when you first login after fresh installation or go to Settings, under the Personal category, click on Online Accounts.
28 Learn DNF
Since Fedora 22 the default package manager has been replaced with “DNF” which stands for Dandified yum (yum was the old package manager). If you haven’t got familiar with that package manager yet, then now is the time to read our extensive guide here:
Conclusion
The above points should be enough to add some flavour to your Fedora Workstation without having too much bloatware. If you think we have missed something or would like us to add further explanation, please use the comment section below.