In this article, we will go through the various steps to install the constituent packages in the LAMP stack with PHP 8.3 and MariaDB 11 on Ubuntu 24.04 Server and Desktop editions.
As you may already know, the LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB, PHP) stack is an assortment of leading open source web development software packages.
This web platform is made up of a web server, a database management system, and a server-side scripting language, and is acceptable for building dynamic websites and a wide range of web applications.
One of the common uses of the LAMP stack is for running content management systems (CMSs) such as WordPress, Joomla, or Drupal, and many others.
Requirements
To follow this LAMP stack tutorial, you’ll need an Ubuntu 24.04 server. If you don’t have one, we recommend getting a VPS (Virtual Private Server) from a reliable cloud provider:
- DigitalOcean – Starting at $4/month, includes $200 in credits for 60 days for new users.
- Linode (Akamai) – Starting at $5/month, includes $100 in credits for 60 days for new users.
Step 1: Install Apache on Ubuntu 24.04
The first step is to start by installing the Apache web server from the default Ubuntu official repositories by typing the following commands on the terminal:
sudo apt update sudo apt install apache2
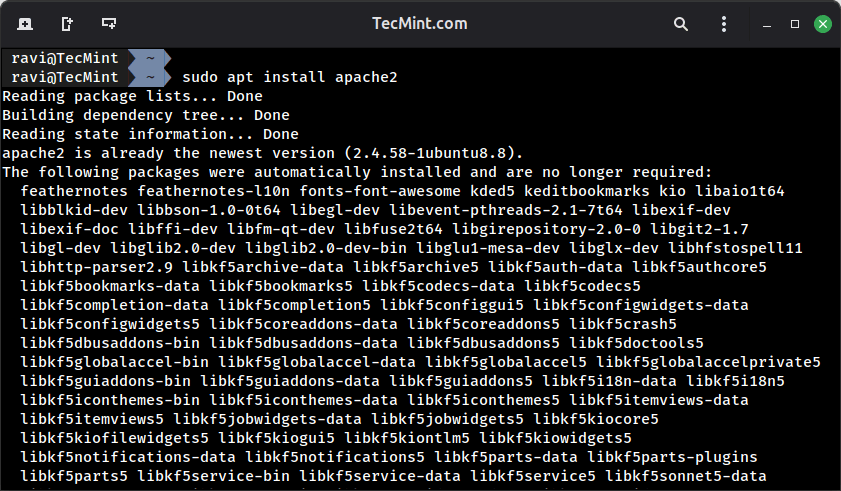
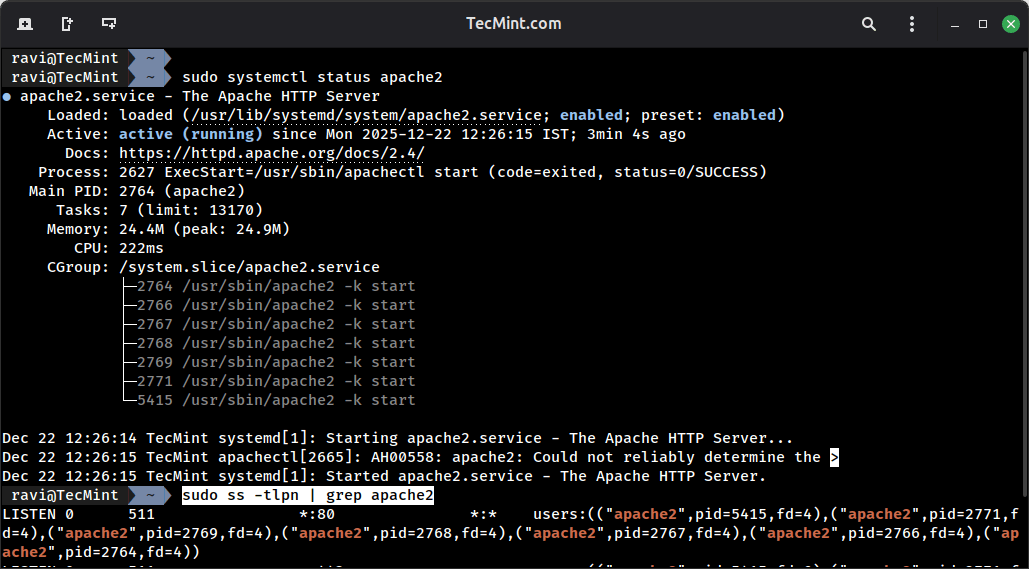
After the Apache web server is successfully installed, confirm if the daemon is running and on what ports it binds (by default apache listens on port 80) by running the commands below:
sudo systemctl status apache2 sudo ss -tlpn | grep apache2
If you have UFW firewall enabled on Ubuntu 24.04, you need to allow HTTP and HTTPS traffic:
sudo ufw allow 'Apache Full' sudo ufw status
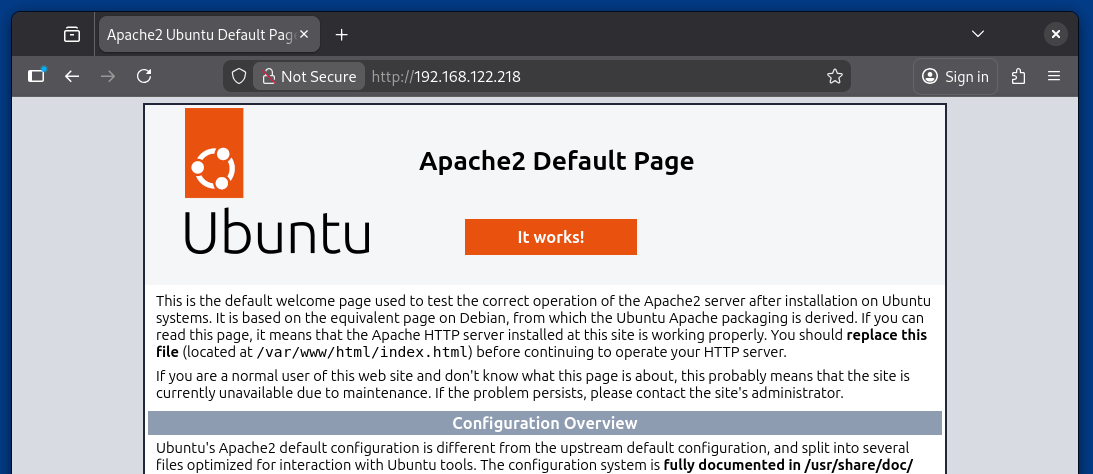
You can also confirm apache web server via a web browser by typing the server IP address using the HTTP protocol. A default Apache web page should appear in the web browser, similar to the below screenshot:
http://your_server_IP_address
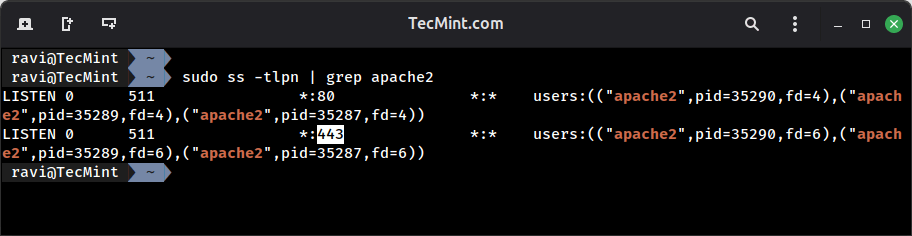
If you want to use HTTPS support to secure your web pages, you can enable the Apache SSL module and confirm the port by issuing the following commands:
sudo a2enmod ssl sudo a2ensite default-ssl.conf sudo systemctl restart apache2 sudo ss -tlpn | grep apache2
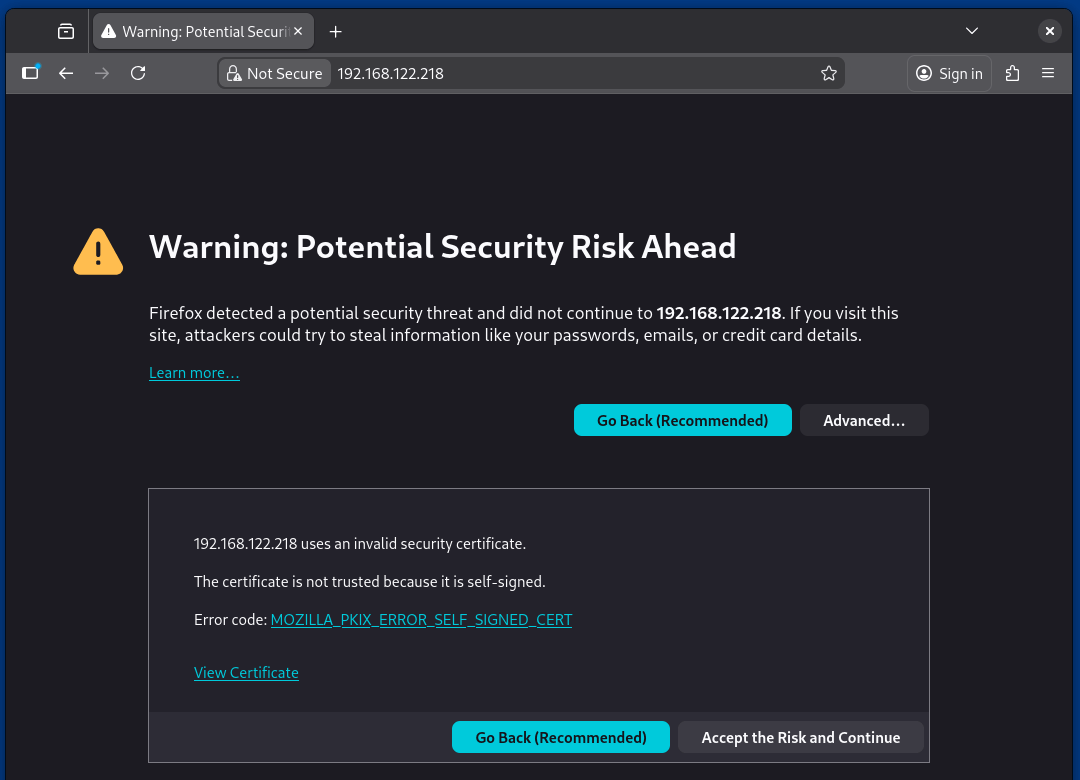
Now confirm Apache SSL support using HTTPS Secure Protocol by typing the below address in a web browser:
https://your_server_IP_address
You will get the following error page, it’s because that apache is configured to run with a Self-Signed Certificate, so just accept and proceed further to bypass the certificate error, and the web page should be displayed securely.
Next, enable apache web server to start the service at boot time using the following command.
sudo systemctl enable apache2
Step 2: Install PHP 8.3 on Ubuntu 24.04
To install PHP with the most commonly needed modules for web development, first do a search for available PHP packages by running the below commands:
apt search php8.3
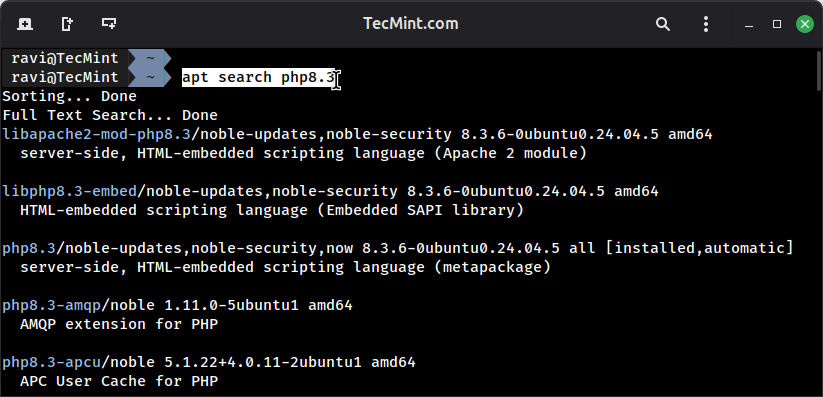
Once you come to know that proper PHP 8.3 modules are needed to set up, use the following command to install the proper modules so that PHP can able to run scripts in conjunction with apache web server.
sudo apt install php8.3 libapache2-mod-php8.3 php8.3-mysql php8.3-xml php8.3-gd php8.3-curl php8.3-mbstring php8.3-zip

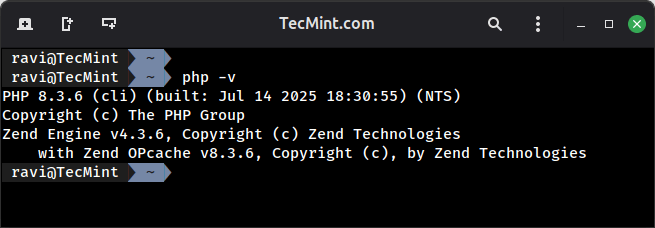
After PHP 8.3 and its required modules are installed and configured on your server, run php -v command in order see the current release version of PHP.
php -v
To further test PHP 8.3 and its module configuration, create a info.php file in apache /var/www/html/ webroot directory with nano text editor.
sudo nano /var/www/html/info.php
Add the below lines of code to info.php file.
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Restart apache service to apply changes.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
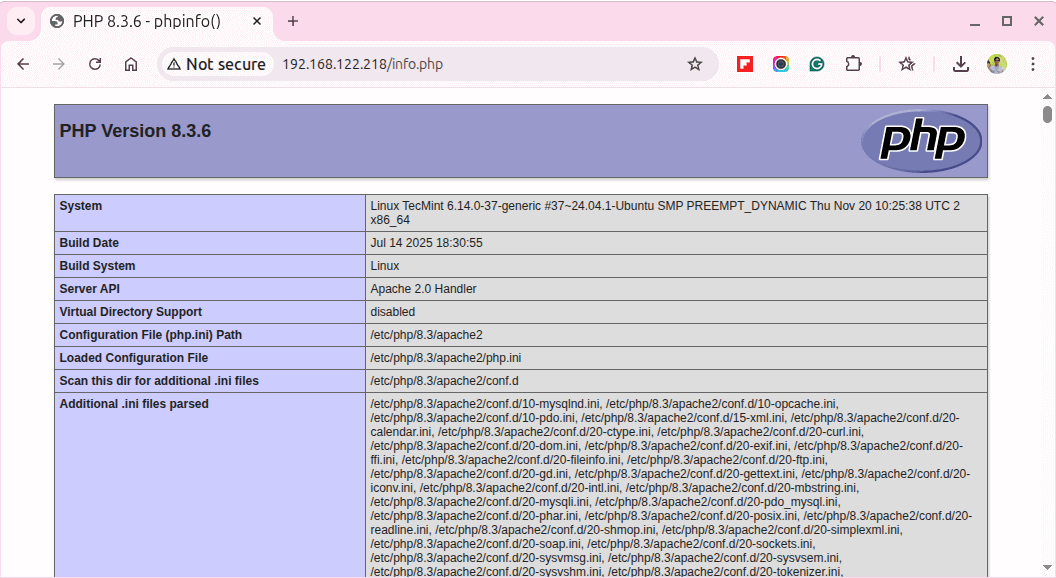
Open your web browser and type the following URL to check the PHP configuration.
http://your_server_IP_address/info.php
If you wanted to install additional PHP modules, use apt command and press [TAB] key after php8.3 string, and the bash autocomplete feature will automatically show you all available PHP 8.3 modules.
sudo apt install php8.3[TAB]
For example, if you need to install additional modules for image processing and internationalization support, you can install them as shown.
sudo apt install php8.3-imagick php8.3-intl php8.3-bcmath
After installing any new PHP modules, always restart Apache to load them.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Step 3: Install MariaDB 11 in Ubuntu 24.04
Now it’s time to install the latest version of MariaDB with the needed PHP modules to access the database from the Apache-PHP interface.
sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client php8.3-mysql
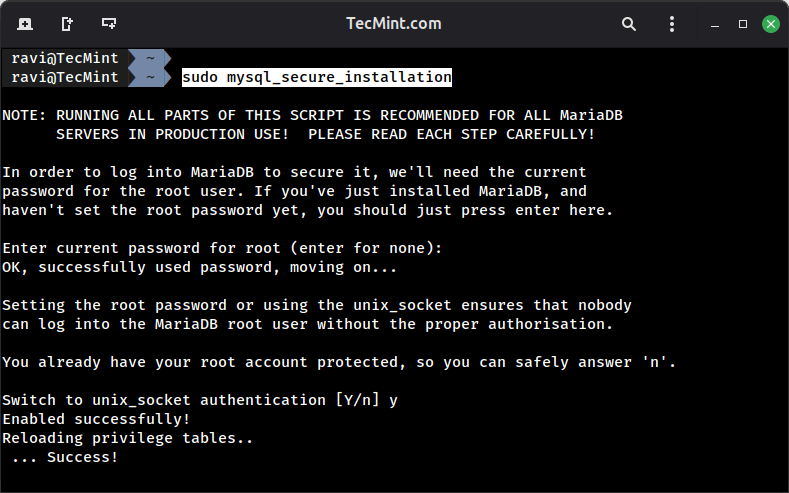
Once MariaDB has been installed, you need to secure its installation using the security script, which will set a root password, revoke anonymous access, disable root login remotely, and remove the test database.
sudo mysql_secure_installation
When prompted:
- Press
Enterfor current password (none by default). - Type
Yto switch to unix_socket authentication (recommended). - Type
Yto set root password and enter a strong password. - Type
Yto remove anonymous users. - Type
Yto disallow root login remotely. - Type
Yto remove test database. - Type
Yto reload privilege tables.
In order to give MariaDB database access to system normal users without using sudo privileges, log in to the MySQL prompt using root, and run the below commands:
sudo mysql
use mysql;
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED VIA mysql_native_password USING PASSWORD('your_strong_password');
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;
To learn more about MariaDB basic usage, you should read our series: MariaDB for Beginners
Then, restart the MariaDB service and try to log in to the database with root as shown.
sudo systemctl restart mariadb mysql -u root -p
Step 4: Install phpMyAdmin in Ubuntu 24.04
Optionally, if you wanted to administer MariaDB from a web browser, install phpMyAdmin.
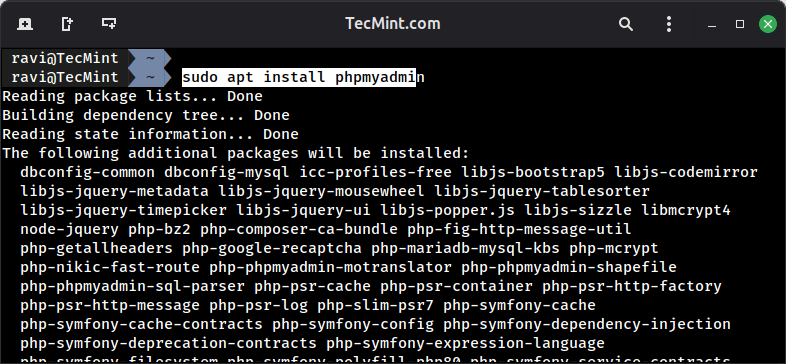
sudo apt install phpmyadmin
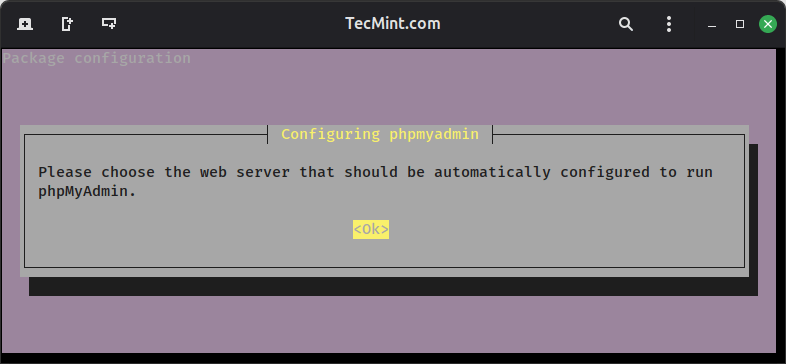
During the phpMyAdmin installation:
- Select
apache2web server (pressSpaceto select, thenEnter). - Choose Yes for configure phpmyadmin with dbconfig-common.
- Enter your
MariaDBroot password when prompted. - Set a strong password for the phpMyAdmin application.
After phpMyAdmin has been installed, you need to enable the necessary PHP extensions and restart Apache:
sudo phpenmod mbstring sudo systemctl restart apache2
You can access the web interface of phpMyAdmin at the below URL:
http://your_server_IP_address/phpmyadmin/
If you want to secure your PhpMyAdmin web interface, go through our article: 4 Useful Tips to Secure PhpMyAdmin Web Interface.
That’s all! Now you have a complete LAMP stack setup installed and running on Ubuntu 24.04, which enables you to deploy dynamic websites or applications on your Ubuntu server.






my phpmyadmin not open in web browser after installing phpmyadmin .
@Waqas
Try to reinstall it, follow the instructions carefully. It should work.
Hi Aaron,
I got the same problem. I reinstalled phpmyadmin, but the same result: /phpmyadmin was not found on this server.
What could be the problem.
Thank you in advance,
Gerard
@Gerard
Try to manually enable phpMyAdmin by copying its apache configuration file located in /etc/phpmyadmin/ path to Apache webserver available configurations directory, located in /etc/apache2/conf-available/:
Then try to access it once more.