Audio and Video are two common sources of information sharing we see in today’s world. May it be publishing any product, the need to share information with a large community of people, or a way of socializing in a group, audio and video have become indispensable.
In the context of sharing knowledge, such as in online tutorials, audio, and video hold a significant place in this highly expressive world. People are eager to share their ideas, prove themselves, and take all possible steps to bring themselves into the limelight.
Video players are the channel for people to see videos. There is a huge list of uses of these videos in our lives, a few of them namely being: watching movies, online tutorials, broadcasting a social message to a huge mass of people, for fun and laughter (i.e. funny short videos), name a few.
Below is a list of high-quality open-source video players available on Linux. While most video players may differ primarily in their user interface, their backend, which is often composed of shared libraries, remains consistent across many, if not all, players.
Thus, the most distinguishable features in video players are the UI, followed by the libraries used internally. Additionally, any unique features that a particular player supports can also attract attention. Based on these factors, we have shortlisted the following video players:
1. VLC Media Player
Initially released in 2001 under the VideoLAN project, VLC Media Player is one of the most powerful media players which is available on a large number of OS including but not limited to Linux, Windows, Solaris, Android, iOS, Syllable, etc.
It is written in C, C++, and Objective C and released under GNU GPLv2+ and GNU LGPLv2.1+. It supports a large number of encoding/decoding libraries avoiding the need for calibrating any kind of plugins.
VLC supports a wide variety of audio and video formats including subtitle support. It is one of the few players providing support for DVDs on Linux.
Other features include: providing the ability to play .iso files so that users can play files on a disk image directly, the ability to play high-definition recordings of D-VHS tapes, can be installed and run directly from a USB flash drive or external drive, and its functionality can be extended via Lua scripting.
Also, apart from all this, VLC also provides API support by providing various APIs, and browser plugin support in Mozilla, Google Chrome, Safari, etc.

Install VLC in Debian, Ubuntu & Linux Mint
To install VLC on Debian-based distributions such as Ubuntu, or Linux Mint, you can use the apt package manager or snap (software).
$ sudo apt install vlc -y OR $ sudo snap install vlc
Install VLC in Fedora
To install VLC on Fedora, you have to enable the RPM Fusion repositories (free and non-free repositories) as shown.
# dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm # dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm # dnf update # dnf install vlc
Install VLC in RHEL Systems
To install VLC on RHEL-based distributions such as CentOS, AlmaLinux, and Rocky Linux, you need to enable the EPEL and RPM Fusion repositories as shown.
-------------- On RHEL 9 Systems -------------- # yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm # yum install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/el/rpmfusion-free-release-9.noarch.rpm # yum install vlc
-------------- On RHEL 8 Systems -------------- # yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm # yum install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/el/rpmfusion-free-release-8.noarch.rpm # yum install vlc
-------------- On RHEL 7 Systems -------------- # subscription-manager repos --enable "rhel-*-optional-rpms" --enable "rhel-*-extras-rpms" # Only needed for RHEL # yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm # yum install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/el/rpmfusion-free-release-7.noarch.rpm # yum install vlc
2. XBMC – Kodi Media Center
Formerly known as Xbox Media Center (XBMC) and now Kodi, this cross-platform player is available under GNU General Public License and in 69+ languages. It is written with C++ as a core with Python scripts as add-ons available.
It allows complete flexibility to the user to play both audio and video files from internet podcasts and all media player files from both local and network storage.
The open-source nature of Kodi has helped it gain a lot of popularity as modified parts of this software are being used along with JeOS as an application suite or framework in a variety of devices including Smart TV, set-top boxes, network-connected media players, etc.
It provides a lot of features as addons which are added as python scripts which include: audio and video streaming plugins, screensavers, visualizations, themes, etc. It provides support of a lot of formats including Audio Formats like MIDI, MP2, MP3, Vorbis, etc., and Video formats including MPEG-1,2,4, HVC, HEVC, RealVideo, Sorenson, etc.
Install Kodi in Debian, Ubuntu & Linux Mint
$ sudo apt-get install software-properties-common $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:team-xbmc/ppa $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install kodi
Install Kodi in Fedora
# dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm # dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm # dnf install kodi
3. SMPlayer – Free Media Player
SMPlayer is another cross-platform media player and a graphical front end for the likes of Mplayer and its forks, written purely using the Qt library in C++. It is available in multiple languages and only on Windows and Linux OS, released under GNU General Public License.
It provides support for all the default formats as in other media players. Talking about its features it provides support for EDL files, configurable subtitles, numerous skins, a YouTube browser, multiple speed playback, audio, and video filters, and equalizers.
Install SMPlayer in Debian, Ubuntu & Linux Mint
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:rvm/smplayer $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install smplayer smplayer-themes smplayer-skins
Install SMPlayer in Fedora
# dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm # dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm # dnf install smplayer
4. MPV Player
Written in C, Objective-C, Lua, and Python, MPV is another free and cross-platform media player released under GPLv2 or later with the latest stable release being v0.36.0.
It is based on MPlayer and focuses mainly on modern systems which have led to advancements in the original code of MPlayer and the introduction of new features.
The transformation from MPlayer to MPV player has led to the deprecation of “slave mode” which was earlier part of MPlayer but now has been discontinued due to broken compatibility.
Instead of this, MPV can now be compiled as a library that exposes client API for better control. Other features include media encoding functionality, smooth-motion which is a form of interpolation between two frames for a smooth transition between them.
Install MPV Player in Debian, Ubuntu & Linux Mint
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:mc3man/mpv-tests $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install -y mpv
Install MPV Player in Fedora
# dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm # dnf install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm # dnf install mpv
5. Gnome Videos
Formerly known as Totem, Gnome Videos is the default media player for Gnome-based desktop environments, It was written purely in C and uses GTK+ and clutter libraries.
From the initial stages only, its development was in two stages, one stage used the GStreamer multimedia framework for playback, and another version (> 2.7.1) was configured to use xine libraries as a backend.
Although the Xine version had better DVD compatibility but was discontinued as the GStreamer version evolved many folds over time with the introduction of DVD-compatible features, and its ability to support a wide variety of formats including playlist formats like SHOUTcast, M3U, SMIL, Windows Media Player format, and Real Audio format.
Other features include: still capturing, loading of SubRip subtitles, ability to adjust brightness, contrast, and saturation during playback. GNOME 3.12 added support for direct video playback from online channels like Guardian and Apple.
Install Gnome Videos in Linux
$ sudo apt install totem [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install totem [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/totem [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add totem [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S totem [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install totem [On OpenSUSE]
6. MPlayer
MPlayer is another multi-lingual cross-platform media player developed by the MPlayer team, available for Linux, Mac, Windows, and even other systems. It is purely written in C and released under the GNU General Public License.
In itself, it is a command-line media player that has the ability to play: video, and audio from physical media like DVD, CD, etc., and local file system.
In the case of videos, it can play lots of video input file formats including CINEPAK, DV, H.263, MPEG, MJPEG, and Real Video, and even is able to easily store the streamed content to a file locally.
Other features that make it one of the great media players include: supporting a variety of output driver protocols like X video extension, DirectX, VESA, Framebuffer, SDL, etc., and easy integration with multiple GUI front-ends written in GTK+ and Qt.
MEncoder which can take input files or stream and can translate into any output format after applying various transformations and subtitle support for Videos.
Install MPlayer in Debian, Ubuntu & Linux Mint
$ sudo apt install mplayer mplayer-gui
Install MPlayer in Fedora
$ sudo dnf install mplayer mplayer-gui mencoder
Install MPlayer in Arch Linux
$ sudo pacman -S mplayer-gui
7. Xine Multimedia Player
Xine is a multimedia player written purely in C and built around a shared library xine-lib that supports multiple configurable frontends.
The development of the Xine project dates back to the year 2000 when even running DVDs was a manual and tedious process. Other media players that share the same library as Xine are Totem and Kaffeine.
Apart from supporting physical media, container formats like 3gp, Matroska, MOV, Mp4, Audio formats, and Network Protocols, Xine also supports various Video Devices like V4L, DVB, PVR, and Various Video formats like Cinepak, DV, H.263, MPEG series, WMV, etc.
One advantage of this media player is its ability to manually correct audio and video stream synchronization.
Install Xine in Debian, Ubuntu & Linux Mint
sudo apt-get install xine-ui -y
Install Xine in Fedora
$ sudo dnf install xine-ui
8. ExMPlayer
ExMPlayer is a beautiful, robust GUI front-end for MPlayer that offers several media management tools including auto converter, audio extractor, and media cutter.
It has playback support for 3D and 2D video and is capable of playing DVD and VCD files, AAC and OGG Vorbis formats, boosting volume by 5000%, subtitle search, etc.
Install ExMPlayer in Debian, Ubuntu & Linux Mint
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:exmplayer-dev/exmplayer $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install exmplayer
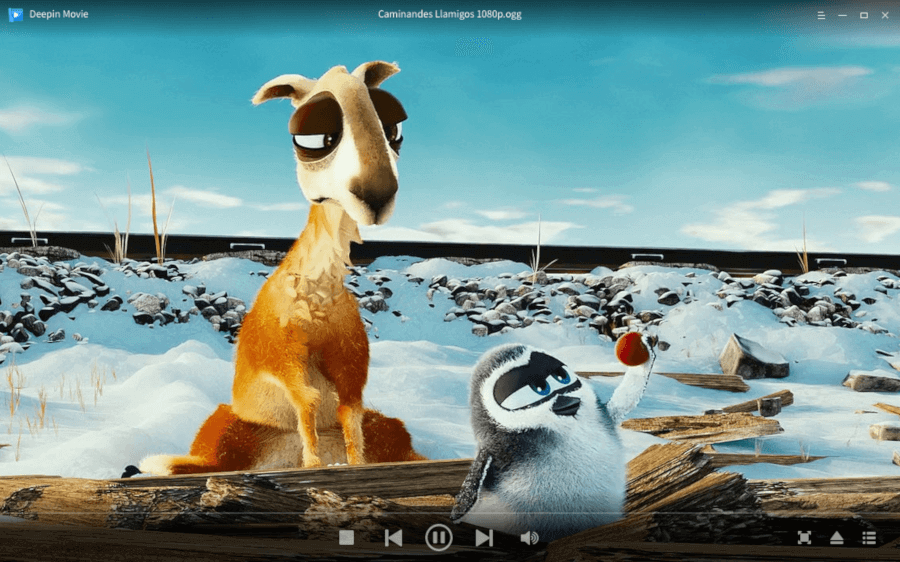
9. Deepin Movie
Deepin Movie is a beautiful open-source media player created for users to enjoy watching several video formats as easily as possible. It was developed for the Deepin Desktop Environment and can be operated completely with only keyboard shortcuts, and streams online videos.

Install Deepin Movie in Linux
$ sudo apt install deepin-movie [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install deepin-movie [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/deepin-movie [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add deepin-movie [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S deepin-movie [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install deepin-movie [On OpenSUSE]
10. Dragon Player
Dragon Player is a simple media player created for playing multimedia files, especially on KDE. It features a beautiful, non-intrusive UI with brightness and contrast settings, support for CDs and DVDs, automatic loading of subtitles, and playback history for resuming videos from the last watched timestamp.
Install Dragon Player in Linux
$ sudo apt install dragonplayer [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install dragonplayer [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/dragonplayer [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add dragonplayer [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S dragonplayer [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install dragonplayer [On OpenSUSE]
11. Celluloid
Celluloid (previously known as GNOME MPV) is a simple media player and GTK+ frontend for MPV, that aims to be simple to use while keeping a high level of configurability.

Install Celluloid in Ubuntu & Linux Mint
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:xuzhen666/gnome-mpv sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install celluloid
12. Parole Media Player
Parole is a modern easy-to-use media player based on the GStreamer framework and written well enough to fit well in the Xfce desktop environment. It is developed with speed, simplicity, and resource usage in mind.
It features playback of local media files, support for a video with subtitles, Audio CDs, DVDs, and live streams, and can be extensible via plugins.

Install Parole in Ubuntu & Linux Mint
$ sudo apt install parole
13. Haruna Video Player
Haruna Video Player is a free and open-source media player for Linux that is based on the Qt/QML framework and the libmpv library.
It is a lightweight and fast player that supports a wide range of media formats, including MP4, MKV, AVI, and FLAC. It also has a number of features that make it a powerful media player, such as the ability to play online videos using youtube-dl, the ability to create playlists, and the ability to adjust the video and audio output.
Install Haruna Video Player in Linux
To install Haruna, you can use flatpak to install it on any Linux distribution using the following commands.
$ flatpak install flathub org.kde.haruna $ flatpak run org.kde.haruna
14. Clapper – GNOME Media Player
Clapper is a free and open-source media player for GNOME, which is built using GJS with the GTK4 toolkit and powered by GStreamer with OpenGL rendering.
It supports a wide range of media formats, including MP4, MKV, AVI, and FLAC. It also supports hardware acceleration, which can improve playback performance on modern computers.
Install Clapper Media Player in Linux
To install Clapper, you can use flatpak to install it on any Linux distribution using the following commands.
$ flatpak install flathub com.github.rafostar.Clapper $ flatpak run com.github.rafostar.Clapper
15. QMPlay2
QMPlay2 is a free and open-source video and audio player for Linux, macOS, and Windows, which is based on the Qt framework and uses the FFmpeg library for decoding media files.
It supports a wide range of media formats, including MP4, MKV, AVI, and FLAC. It also supports hardware acceleration, which can improve playback performance on modern computers.
Install QMPlay2 Media Player on Linux
To install QMPlay2, you can use AppImage, which is a portable version of the QMPlay2 media player that can be run on any Linux distribution without installation.
First download QMPlay2 AppImage, make it executable, and run it as shown.
$ chmod +x QMPlay2-*.AppImage $ ./QMPlay2-*.AppImage
16. Kaffeine Media Player
Kaffeine is a free and open-source media player for Linux, which is based on the Qt framework and uses the GStreamer multimedia framework for decoding media files.
Install Kaffeine Media Player in Linux
$ sudo apt install kaffeine [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install kaffeine [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/kaffeine [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add kaffeine [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S kaffeine [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install kaffeine [On OpenSUSE]
Conclusion
These are some selected video players which are available on the Linux platform. If you use any other video player, do write to us in the comments and we will include it in our list.


I have KDE Neon Linux operating system and have problems with VLC and my Radeon graphics card. Other players that are installed include a smplayer, MPlayer, and MPV media player, but only VLC supports the DVD menu where I can use my mouse to select an episode from the menu.
When I try this in all of the other players, nothing happens. The only way to play an episode is to open the
.vobfile from the video folder. A nuisance. Besides VLC, do any of the above-suggested players support a DVD menu?Miro caught my interest but unfortunately, I can’t install it. When tried I got this errors
The following packages have unmet dependencies: miro : Depends: libavcodec53 (>= 4:0.8-1~) but it is not installable or libavcodec-extra-53 (>= 4:0.8-1~) but it is not installable Depends: libavformat53 (>= 4:0.8-1~) but it is not installable or libavformat-extra-53 (>= 4:0.8-1~) but it is not installable Depends: libavutil51 (>= 4:0.8-1~) but it is not installable or libavutil-extra-51 (>= 4:0.8-1~) but it is not installable Depends: libtag1c2a (>= 1.5) but it is not installable Depends: python-support (>= 0.90.0) but it is not installable Depends: python-gst0.10 but it is not installable Depends: python-webkit but it is not installable Depends: gstreamer0.10-ffmpeg but it is not going to be installed Depends: gstreamer0.10-plugins-base but it is not installable Depends: gstreamer0.10-plugins-good but it is not installable Depends: gstreamer0.10-plugins-bad but it is not installable Depends: gstreamer0.10-plugins-ugly but it is not installable Depends: gstreamer0.10-x but it is not installable Depends: libgstreamer0.10-0 but it is not installable Depends: libtag1-vanilla but it is not installable Depends: libtorrent-rasterbar5 but it is not installable or libtorrent-rasterbar6 but it is not installable E: Unable to correct problems, you have held broken packages.So for now Debian has no audiovisual player as nightingale and banshee are deprecated and do not work any longer. The only option left is Kodi but its Ui is more suited for the big screen, not desktop.
I just tried to install most of these, and very few ran. You may want to update as none of this was helpful to me.
Snappy minimalistic video player
Re: Kodi I tried to install it on Ubuntu and it complains about the Python Cryptography module version …
Why is mplayer’s screenshoot a windows one? Isn’t this Linux?!
Not sure you should bring Kodi to the table. Usually Kodi depends on other players. It might be correct that internally, it’s able to play media files. But in my opinion it is a media center and not a media player.
mplayer, kmp, vlc, and certain os based players, are more truly media players. Seems a bit too much like putting a banana in a bag and asking you to eat the bag.As Kodi is able to play media by itself (I think it is) you are partly correct,but I still think it is another kind of product.
I have video file on SMB share with visual aspect ratio about 2:1 (long time ago it was 16:9) and frame aspect ratio 4:3.
In Windows I just rum MPC-HC, open \\nas\share\video.avi and use numpad to adjust sizes.
Is there ANY linux player that can do this? I don’t want to mount.cifs that share and convert file to normal frame size, I just want to watch video. From Dolphin context menu :-)
i like smplayer’s ability to navigate video track using keyboard arrow keys, but i hate it for pulling too much dependencies. thanks to mplayer2 i have to install the unwanted whole samba packages because mplayer2 depends on libsmbclient in debian (or smbclient in arch linux). if only them developers can move that foocking samba dependencies to an add-on mplayer2/smplayer would be my favourite player
Wonderful list. I like VLC more compared to other free video players. Tested already from windows to mac and linux.