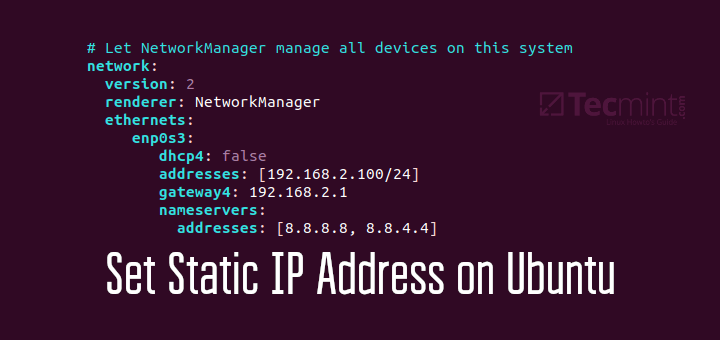
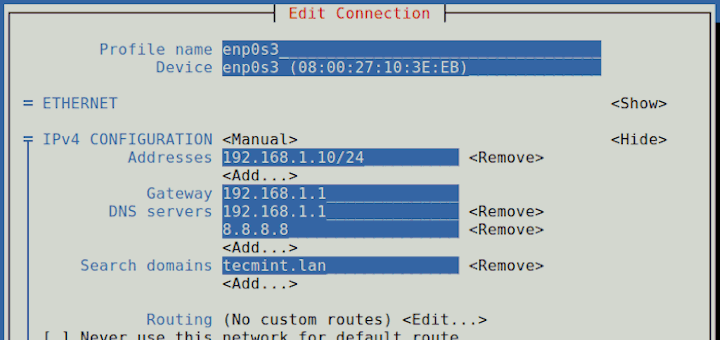
It’s usually a good idea to configure essential network services to automatically start on boot. This saves you the hassle of starting them manually upon a reboot and also, the resulting havoc caused in case you forget to do so. Some of the crucial network services include SSH, NTP, and httpd.
You can confirm what is your system service manager by running the following command.
# ps --pid 1
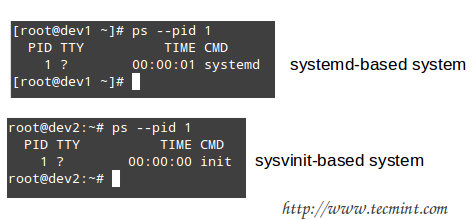
Based on the output of the above command, you will use one of the following commands to configure whether each service should start automatically on boot or not:
On systemd-based
----------- Enable Service to Start at Boot ----------- # systemctl enable [service]
----------- Prevent Service from Starting at Boot ----------- # systemctl disable [service] # prevent [service] from starting at boot
On sysvinit-based
----------- Start Service at Boot in Runlevels A and B ----------- # chkconfig --level AB [service] on
----------- Don’t Start Service at boot in Runlevels C and D ----------- # chkconfig --level CD service off
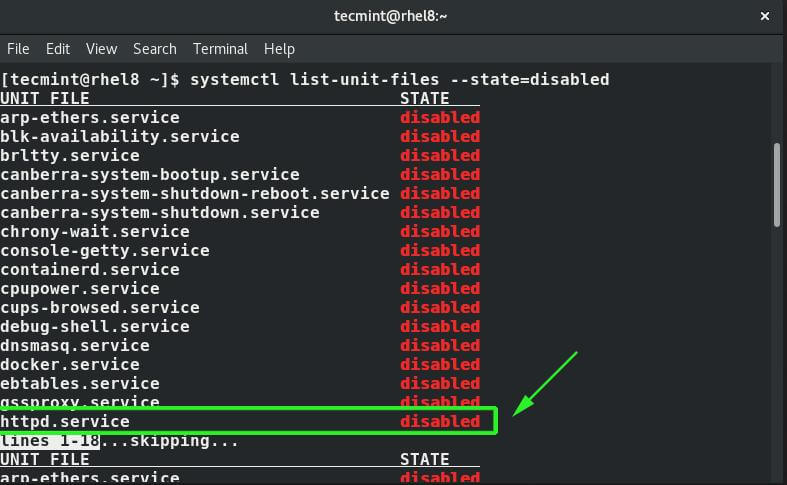
On a systemd system like CentOS 8, RHEL 8 and Fedora 30+, the systemctl command is used for managing services. For example, to have a view of the disabled services, run the command:
$ sudo systemctl list-unit-files --state=disabled $ sudo chkconfig --list [On sysvinit-based]
The output below prints out all the disabled services and as you can see, the httpd service is listed, implying that it is not configured to start on boot.
To enable a service to start on boot, use the syntax:
$ sudo systemctl enable service-name $ sudo chkconfig service_name on [On sysvinit-based]
For example, to enable httpd service on boot execution.
$ sudo systemctl enable httpd $ sudo chkconfig httpd on [On sysvinit-based]
To confirm that the httpd service has been enabled, list all the enabled services by executing the command:
$ sudo systemctl list-unit-files --state=enabled $ sudo chkconfig --list | grep 3:on [On sysvinit-based]
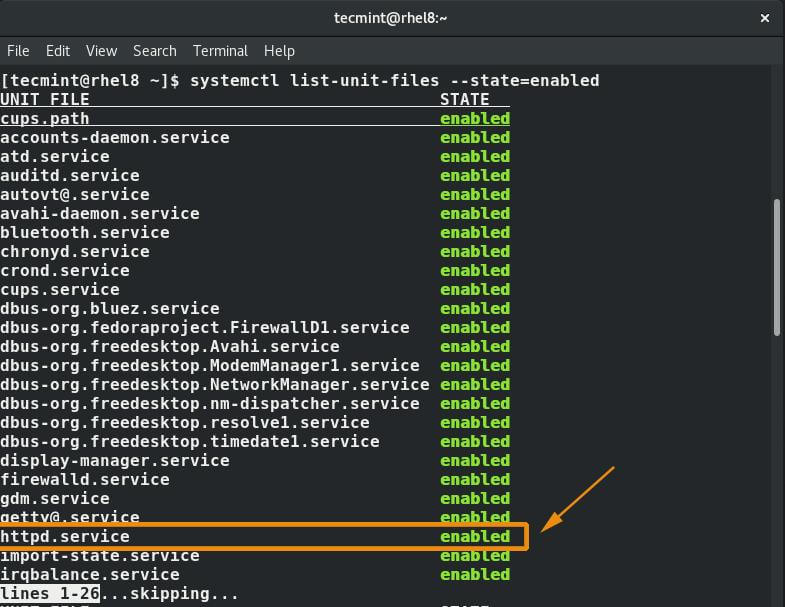
From the output above, we can clearly see that the httpd service now appears in the list of enabled services.
To learn more about systemctl and chkconfig commands, read these following articles: