After installing the components of a LAMP stack on a CentOS/RHEL 7 server, there are a couple of things you may want to do.
Some of them have to do with increasing the security of the Apache and MySQL / MariaDB, while others may be applicable or not according to our setup or needs.
For example, based on the expected use of the database server, we may want to change the default data directory (/var/lib/mysql) to a different location. This is the case when such a directory is expected to grow due to high usage.
Otherwise, the filesystem where /var is stored may collapse at one point causing the entire system to fail. Another scenario where changing the default directory is when we have a dedicated network share that we want to use to store our actual data.
For this reason, in this article, we will explain how to change the default MySQL / MariaDB data directory to a different path on a CentOS/RHEL 7 server and Ubuntu/Debian distributions.
Although we will use MariaDB, the concepts explained and the steps taken in this article apply both to MySQL and to MariaDB unless noted otherwise.
Changing the default MySQL/MariaDB Data Directory
Note: We are going to assume that our new data directory is /mnt/mysql-data. It is important to note that this directory should be owned by mysql:mysql.
# mkdir /mnt/mysql-data # chown -R mysql:mysql /mnt/mysql-data
For your convenience, we’ve divided the process into 5 easy-to-follow steps:
Step 1: Identify Current MySQL Data Directory
To begin, it is worthy and well to identify the current data directory using the following command. Do not just assume it is still /var/lib/mysql since it could have been changed in the past.
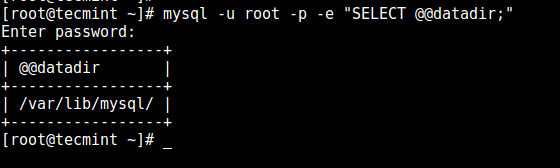
# mysql -u root -p -e "SELECT @@datadir;"
After you enter the MySQL password, the output should be similar to.
Step 2: Copy MySQL Data Directory to a New Location
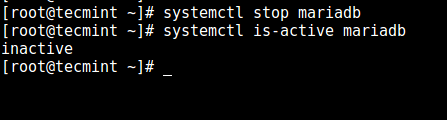
To avoid data corruption, stop the service if it is currently running before proceeding. Use the systemd well-known commands to do so:
------------- On SystemD ------------- # systemctl stop mariadb # systemctl is-active mariadb ------------- On SysVInit ------------- # service mysqld stop # service mysqld status OR # service mysql stop # service mysql status
If the service has been brought down, the output of the last command should be as follows:
Then copy recursively the contents of /var/lib/mysql to /mnt/mysql-data preserving original permissions and timestamps:
# cp -R -p /var/lib/mysql/* /mnt/mysql-data

Step 3: Configure a New MySQL Data Directory
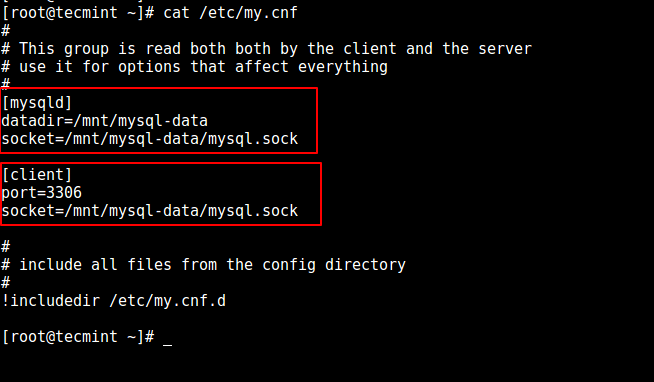
Edit the configuration file (my.cnf) to indicate the new data directory (/mnt/mysql-data in this case).
# vi /etc/my.cnf OR # vi /etc/mysql/my.cnf
Locate the [mysqld] and [client] sections and make the following changes:
Under [mysqld]: datadir=/mnt/mysql-data socket=/mnt/mysql-data/mysql.sock Under [client]: port=3306 socket=/mnt/mysql-data/mysql.sock
Save the changes and then proceed with the next step.
Step 4: Set SELinux Security Context to Data Directory
This step is only applicable to RHEL/CentOS and its derivatives.
Add the SELinux security context to /mnt/mysql-data before restarting MariaDB.
# semanage fcontext -a -t mysqld_db_t "/mnt/mysql-data(/.*)?" # restorecon -R /mnt/mysql-data
Next restart the MySQL service.
------------- On SystemD ------------- # systemctl stop mariadb # systemctl is-active mariadb ------------- On SysVInit ------------- # service mysqld stop # service mysqld status OR # service mysql stop # service mysql status
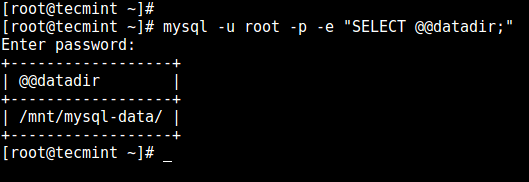
Now, use the same command as in Step 1 to verify the location of the new data directory:
# mysql -u root -p -e "SELECT @@datadir;"
Step 5: Create MySQL Database to Confirm Data Directory
Login to MariaDB, create a new database and then check /mnt/mysql-data:
# mysql -u root -p -e "CREATE DATABASE tecmint;"
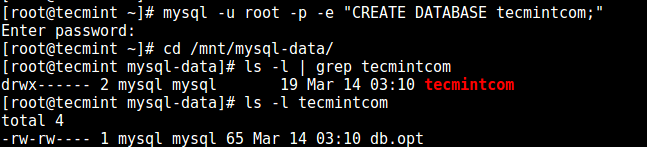
Congratulations! You have successfully changed the data directory for MySQL or MariaDB.
Summary
In this post, we have discussed how to change the data directory in a MySQL or MariaDB server running on CentOS/RHEL 7 and Ubuntu/Debian distributions.
Do you have any questions or comments about this article? Feel free to let us know using the form below – we are always glad to hear from you!






Hi, the part after copying the database files, restart MySQL – commands need revision.
Error in part 3 you say my.cnf but in the commands, you use my.conf this may be confusing…
@Paul,
Thanks, corrected the command in the article…
Hi!
I followed step to step but when I try to boot the services it doesn’t work :(
2021-02-05 11:20:29 0 [Note] Server socket created on IP: ‘::’.
2021-02-05 11:20:29 0 [ERROR] Can’t start server : Bind on unix socket: Operation not permitted
2021-02-05 11:20:29 0 [ERROR] Do you already have another mysqld server running on socket: /mnt/datos/mysql.sock ?
2021-02-05 11:20:29 0 [ERROR] Aborting
any idea?
Thanks! Ring the bell, you’ve saved another one!
Interesting: followed all the steps and received a message that MariaDB “can’t create a test file” in the new directory. Something with directory permissions?
If you are moving to a folder under the home partition and you are using systemd to start the database service, then this error can occur.
You need to create a folder with:
Then create a file there with:
Run:
and you should be all set if the home folder restriction was your problem.
Thanks a lot for this tutorial.
I actually ran out of space and was trying to move the data directory to a new drive. I browsed through many blogs and followed the steps but was getting the below error “couldn’t find aria_log_control“.
The step: Setting the SELinux security context to the new data directory solved my problem.
Hi, Thanks for a really useful tutorial. The moving the DB part worked really well, but when I try and move the socket there seems to be a problem accepting client connections. phpMyAdmin returns “Cannot Logon to the MYSQL server” – mysqli_real_connect(): (HY000/2002): No such file or directory.
If I leave the socket in the default dir “/run/mysql/mysql.sock” I get no problems.
I have the following in my.cnf:
MYSQL starts OK and I can run sql from the terminal for example :
I don’t think ownership permissions is the problem:
I also tried configuring it to be in “/mnt/HD2TB/serverdata/mysql/mysql.sock” and I get the same problem. I get the same problem if I chown to
mysql:mysql(I’m not sure what the difference is.Each time I test I do perform: systemctl stop mysql and then start MySQL. I am running on OpenSuse Leap 15.1
Hi
Thank you for this tutorial, I’m glad to find this, but afterward, I tried to perform:
I get the message:
the external SSD-USB-drive show’s drwxrwxrwx on mysql-data. It is different, /mnt/MyDrive/mysql-data or /media/pi/MyDrive/mysql-data?
my system is RPI4 Mod B with Buster, after installing the components and setup of a LAMP-sever
Thank you for all comments
@Max,
All external devices are mounted under /mnt, so that command should be.
Hi,
Ok I have changed this (mnt/MyDrive/mysql-data) after running as user pi:
I get on all item: Operation not permitted
mysql is runnig; @@datadir is /var/libmysql/
for your help
Hi, it’s me again
in the meantime, all is now OK!!! MariaDB Database is no running on my SSD
(after one week trying… I’m very glad)
thank you again for this tutorial
Max
The new version 10.1.15 of the mariadb /etc/my.cnf does not have the datadir. below the what is in the file? Where to the change?
@Dalu,
You can add the datadir location in
my.cnffile.Hi, I had the same problem (Job failed to start).
log: Database MariaDB is not initialized, but the directory /home/data is not empty, so initialization cannot be done.
I did something like that:
1. copy all mysql/mariadb datadir into the: /home/data/mysql
2. mv /var/lib/mysql /var/lib/mysql.bak
3. mkdir /var/lib/mysql
4. mount –bind /home/data/mysql /var/lib/mysql (and save/remember it in fstab)
And It’s working!
Super job It so helped me And we need to install “yum install policycoreutils-python”
if we unable to find *semanage* command. It very helped me a lot. Before i done all steps but not getting proper result.
Because i for got about Selinux group.
1. Stop MySQL, Before making any changes, first make sure to stop mysql service
2. Change Data Directory, Now copy default MySQL data directory (/var/lib/mysql) to other location as per your requirement. Also set the required MySQL ownership on new directory location. As per below command, we are relocating data directory to /data/mysql.
3. Now edit MySQL default configuration file /etc/my.cnf and update values of datadir and socket variable.
4. Start MySQL, After making all above changes. finally, start MySQL service. Now it will use new data directory path.
@Angela Erin I did all the steps you described and I get the message: start: Job failed to start
Any suggestions?
thanks in advance
Can you please share the output of
journalctl -xn
and
systemctl -l status mariadb
right after you attempt to restart the service?
Hi,
A previous attempt to move the MySQL database to the external SSD as described above, I get the ERROR 2002 (HY000) can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket!
I was unable to solve this problem! (new installation!).
@Max,
Make sure that MySQL is running on the server, before moving the databases..