This article is the continuation of our Linux system monitoring series, today we’re talking about the most popular monitoring tool called htop, which is just reached version 3.0.5 and comes with some cool new features.
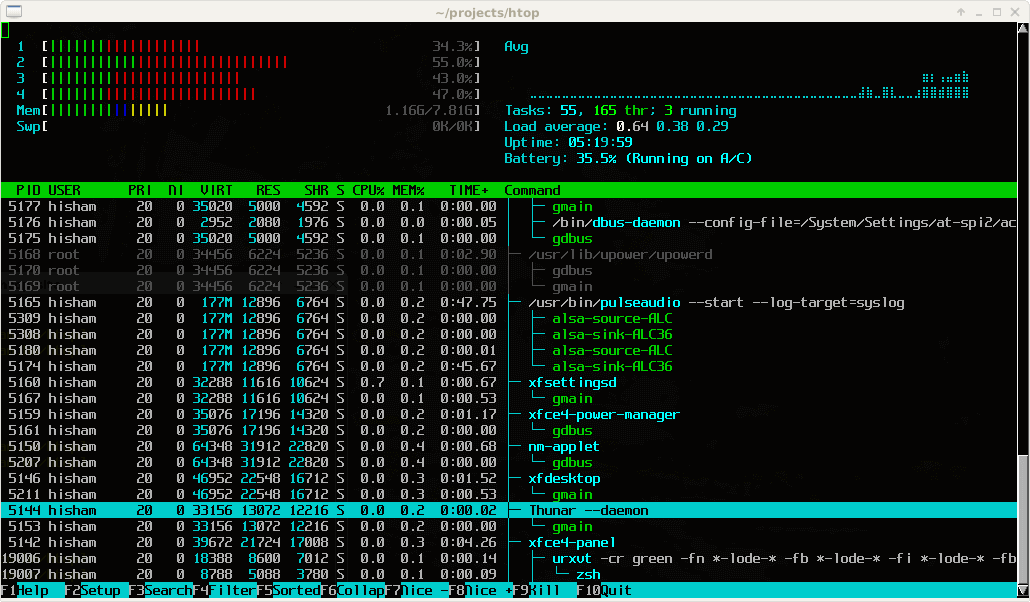
Htop is an interactive real-time process monitoring application for Linux/Unix-like systems and also a handy alternative to top command, which is a default process monitoring tool that comes pre-installed on all Linux operating systems.
Htop has numerous other user-friendly features, which are not available under the top command and they are:
- In htop, you can scroll vertically to view the full process list and scroll horizontally to view the full command lines.
- It starts very quickly as compared to the top because it doesn’t wait to fetch data during startup.
- In htop, you can kill more than one process at once without inserting their PIDs.
- In htop, you no longer needed to enter the process number or priority value to re-nice a process.
- Press “e” to print the set of environment variables for a process.
- Use the mouse to select list items.
Install Htop in Linux
The htop packages are mostly available in all modern Linux distributions and can be installed using the default package manager from your system.
Install Htop on Debian
$ sudo apt install htop
Install Htop on Ubuntu
$ sudo apt install htop
Install Htop on Linux Mint
$ sudo apt install htop
Install Htop on Fedora
$ sudo dnf install htop
Install Htop on CentOS 8/7
$ sudo yum install epel-release $ sudo yum install htop
Install Htop on RHEL 8/7
--------- On RHEL 8 --------- $ sudo yum -y install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm $ sudo yum install htop --------- On RHEL 7 --------- $ sudo yum -y install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm $ sudo yum install htop
Install Htop on Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux
$ sudo yum install epel-release $ sudo yum install htop
Install Htop on Gentoo
$ emerge sys-process/htop
Install Htop on Arch Linux
$ pacman -S htop
Install Htop on OpenSUSE
$ sudo zypper install htop
Compile and Install Htop from Sources in Linux
To build Htop from sources, you must have Development Tools and Ncurses installed on your system, to do so run the following series of commands on your respective distributions.
On RHEL/CentOS and Fedora
$ sudo yum groupinstall "Development Tools" $ sudo yum install ncurses ncurses-devel
On Debian, Ubuntu, and Mint
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential $ sudo apt-get install libncurses5-dev libncursesw5-dev
Next, download the latest htop from the Github repo and run the configure and make a script to install and compile htop.
$ wget -O htop-3.0.5.tar.gz https://github.com/htop-dev/htop/archive/refs/tags/3.0.5.tar.gz $ tar xvfvz htop-3.0.5.tar.gz $ cd htop-3.0.5/ $ ./configure $ make $ sudo make install
How do I use htop?
Now run the htop monitoring tool by executing the following command on the terminal.
# htop
Htop is having three sections mainly
- Header, where we can see info like CPU, Memory, Swap and also shows tasks, load average, and Up-time.
- List of processes sorted by CPU utilization.
- Footer shows different options like help, setup, filter tree kill, nice, quit, etc.
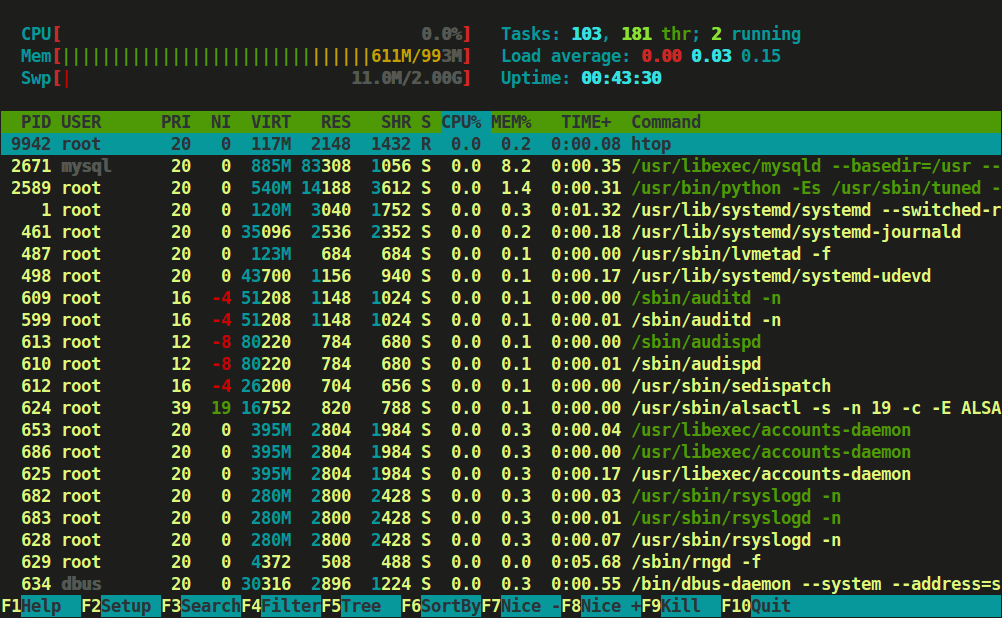
Press F2 or S for setup menu > there are four columns i.e Setup, Left Column, Right Column, and Available Meters.
Here, you can configure the meters printed at the top of the window, set various display options, select among color patterns and choose which columns are printed in which order.
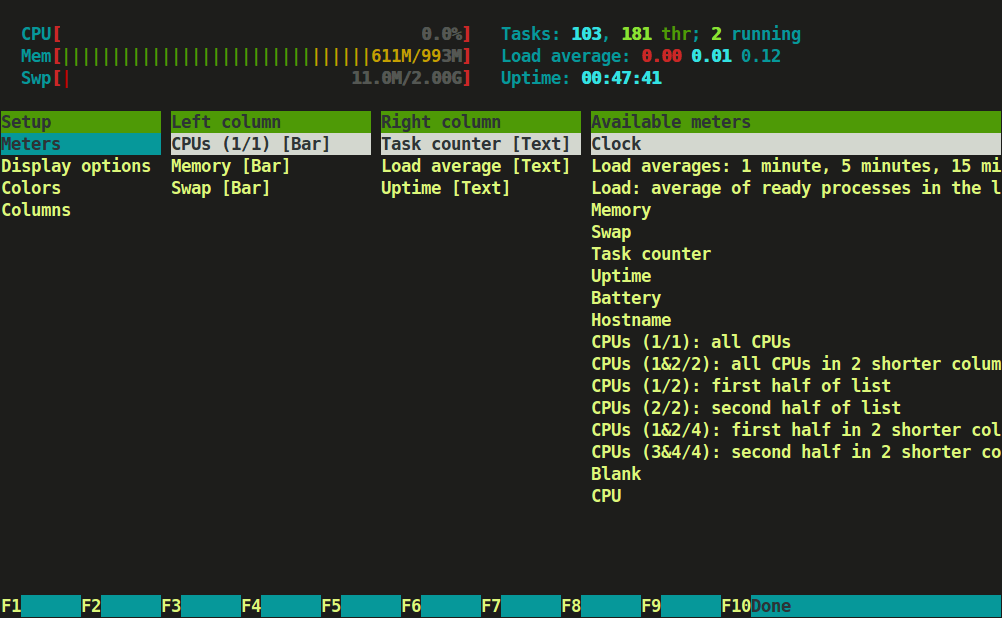
Type tree or t to display processes tree view.
You can refer to function keys displayed at the footer to use this nifty htop application to monitor Linux running processes. However, we advise using character keys or shortcut keys instead of function keys as they may have mapped with some other functions during secure connection.
Htop Shortcut and Function Keys
Some of the shortcut and function keys and their functionality to interact with htop.
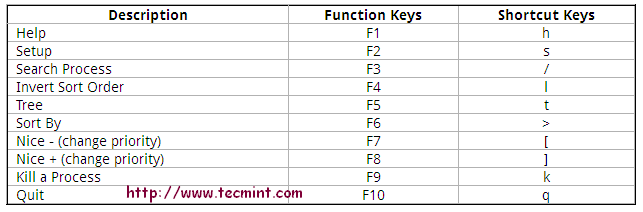




The mentioned method for installing EPEL doesn’t work on CentOS 7 now. The following method works fine:
@Abdollah,
Thanks for the suggestion, I have updated the article…
The latest version of EPEL repository can be installed directly via yum command on RHEL/CentOS 7 systems, using:
Reference: https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/EPEL
Did you forget step of epel.repo file configuration? because we need to make changes into configuration file.
@Madhav,
May I know like what configuration changes for epel.repo? Could you share with us?
I just kept this part out of newly created epel.repo config file, before that, there were some errors in result of:
@Madhav,
Thanks for sharing, hope it will help other users who face similar error..
I found an even easier way to install Epel before yum install htop:
Instead of this:
I just tried this:
it seems to work.
@Philip,
Yeah thanks for sharing, never though the we could install epel this way…:)
Yeah thanks for sharing mate
Can Htop capture cpu process usage on certain period of time what are the process running that cause cpu spike on certain period.
@Daud,
No it can’t capture CPU usage on certain time, its main purpose is to show top running processes, but you can certainly Limit and Control CPU Utilization of Linux Processes Using CPUTool.
New link for centos 7: http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/e/epel-release-7-11.noarch.rpm
@Alx,
Thanks, updated the EPEL link..
CentOS/RHEL 7
New package epel-release-7-10.noarch.rpm
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-10.noarch.rpm
@Sammons,
Thanks for the updated link, corrected in the writeup.
For CentOS/RHEL 7 the package name now is epel-release-7-9.noarch.rpm https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-9.noarch.rpm
I got this error while MAKE
htop-ScreenManager.o: In function `ScreenManager_run’:
/root/htop-2.0.2/ScreenManager.c:192: undefined reference to `set_escdelay’
htop-InfoScreen.o: In function `InfoScreen_run’:
/root/htop-2.0.2/InfoScreen.c:120: undefined reference to `set_escdelay’
collect2: ld returned 1 exit status
make[1]: *** [htop] Error 1
make[1]: Leaving directory `/root/htop-2.0.2′
make: *** [all] Error 2
@Bilal,
On which Linux distribution you are trying to install Htop? have you installed all the required libraries? I mean development tools before compiling htop?
Thank you for this tool…
Bon article !
repoforge.org is down and the project is dead, as discussed in https://github.com/repoforge/rpms/issues/375
Is there any other repo for htop2?
@Axel,
Yes it was dead a long back ago and I forget to update this article, but thanks for notifying the same. I’ve updated the htop article with latest version htop 2.0.2 with installation via EPEL repository..
Hi, Ravi. Which terminal and font do u use? Looks cool and nice
Thanks for the post :)
@Aleks,
I use Oswald Google fonts in my terminal to look nice and clear.
Great article, worked fine on AWS AMI.
Thanks Ravi
The RPM Forge instructions still installed the old version of HTOP, so I built from source (I’m on CentOS 7). It builds okay using your instructions but at the end, you need to say in order to run HTOP this way, you need to run it with a dot-slash:
# ./htop
@Dave,
Even if you use EPEL or any other third party repository, you will get the old version of htop, that’s the reason I’ve included instructions to build from source to get most recent version, but I did tried same instructions on my CentOS 7.0 and I can able to run as:
Your path probably doesn’t include your current directory (represented by a single period/dot). Try typing this and you’ll see what I mean:
echo $PATH
Sample output:
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games
This set of directories is your PATH. When you type a command, your OS will search these directories looking for that command. You would think it would start with your current directory by default, but it doesn’t. Note that the directories are seperated by colons. To include the current working directory, you would have to add this to the end of the PATH:
:.
(A colon then a period/dot)
You can alter your path by editing the rc file for whatever shell you are using. If you don’t know which shell that is, you can try one of two commands to find out:
echo $SHELL
Example output: /bin/bash
or
env | grep ‘SHELL=’
Example output: SHELL=/bin/bash
So in my case I’m using bash, so I would backup the file .bashrc in my home directory
cp ~/.bashrc ~/.bashrc.bak
Then edit the original with a text editor (I use vi, but nano or emacs should work as well):
vi ~/.bashrc
At the bottom of the file (in case there are other export PATH statements in it) add the following statement on a line by itself:
export PATH=$PATH:.
and save the file. Note that your command syntax may vary if you are not using bash as your shell.
Open up a NEW terminal window and type:
echo $PATH
Example output. Note the :. at the end
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:.
Now your current directory should always be part of the path and you won’t need to use ./ to run scripts. Note that this only takes effect when you start a new terminal.
NOTES:
1. To make sure you never lock yourself out of shell, ALWAYS open a new terminal KEEPING YOUR OLD ONE OPEN to verify that your changes worked. And remember, backups are a really good idea.
2. I tested these specific instructions on Linux Mint (a variant of Ubuntu) using the bash shell. I cannot guarantee they will work *exactly* the same everywhere. I can say that I have edited the PATH variable successfully on other linux variants for bash and the technique should be very similar if not identical.
3. Through research I have noted that some prefer to put this type of command in the file .profile or .bash_profile. I have not tried doing this. You can find more info here: http://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/26047/how-to-correctly-add-a-path-to-path
like htop when your in their directory.
Hope this helps!
I follow your guide and has been installed succesfully htop on our cPanel servers. Thank you!
htop
command not found :(
Thank you for TUT.
Can you help me uninstall htop?
Simple, yum remove htop..
there is newer rpmforge package available, the rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1
Thanks for updating me.
# rpm -i rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el6.rf.x86_64.rpm
error: Failed dependencies:
rpmlib(FileDigests) <= 4.6.0-1 is needed by rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el6.rf.x86_64
rpmlib(PayloadIsXz) <= 5.2-1 is needed by rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el6.rf.x86_64
getting error after running all command
Which OS version you using?
Nice,
i prefered a Visual then in terminal
Thank You for your trouble