The automatic creation and management of virtual machines is a topical issue for any company that provides VPS services. If you manage a large number of machines, a command line is definitely not the only tool you may need to perform various operations including client tasks, because such operations may be time-consuming.
In order to simplify the routine tasks of server administrators and users, various companies develop control panels for virtual machine management, including interface-based solutions.
A control panel empowers you to perform any operation with a mouse click, whereas it would take you a good deal of time to complete the same task in the console. With a control panel, you will save time and effort. However, it’s not all that simple.
Nowadays, VMmanager is the most popular software product for small and medium-sized businesses. VMware, in its turn, is a leading solution for large organizations. Both software products are commercial and rather expensive.
They deliver a large number of functions, however, some companies, especially, startups may need them. Besides, many of them cannot afford such an expensive product. For example, startups and companies in times of crisis may experience financial difficulties.
Moreover, one can find interesting, outstanding solutions integrated with billing systems including tools for VM management.
How not to get lost among a great number of offers? We decided to help our users and wrote the following article, in which they will find answers to this question.
In this article, we will describe control panels for virtual machine management, both commercial and open-source, and help you choose the right solution to meet your personal needs.
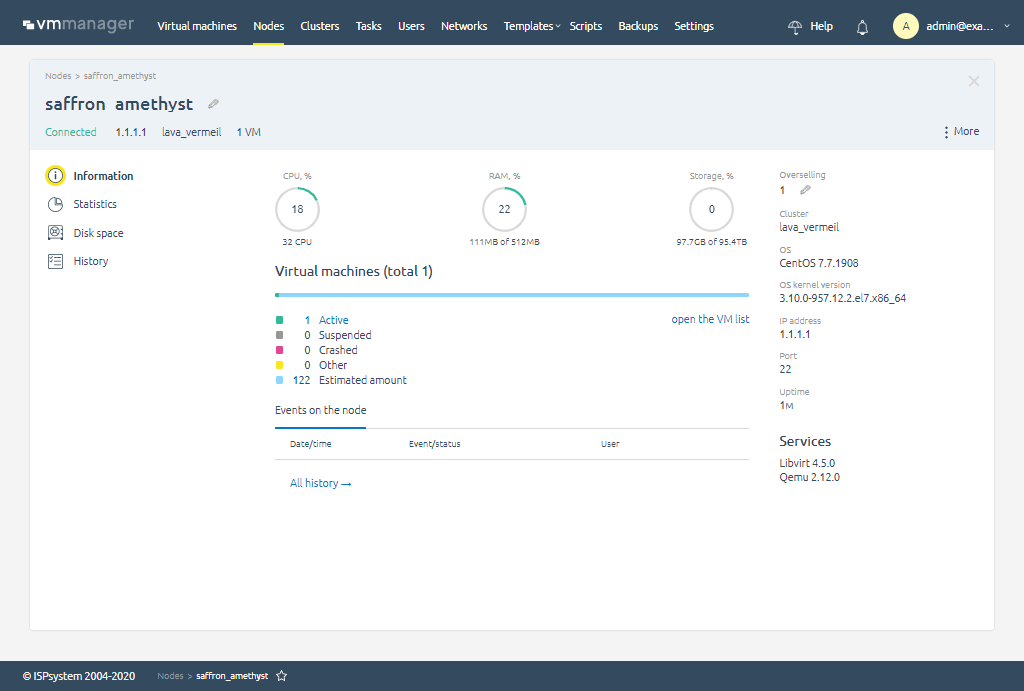
1. VMmanager
VMmanager is one of the most popular commercial server virtualization platforms based on QEMU/KVM technology. The solution has a reach feature set, that can suit both IT infrastructure owners’ and VPS services providers’ needs.
Virtual servers can be created within 2 minutes. Many routine tasks are performed automatically: including migration, cloning, reinstalling the OS, backups, adding and deleting interfaces, virtual server image creation, monitoring, statistics collection, server provisioning, etc.
The main advantages of a VMmanager are:
- Centralized management of various clusters.
- Fault tolerance due to a microservice architecture.
- Overselling, which helps to improve the VPS provider’s equipment efficiency.
- Complete control of the infrastructure thanks to a robust system of metrics collection.
- A modern and intuitive interface.
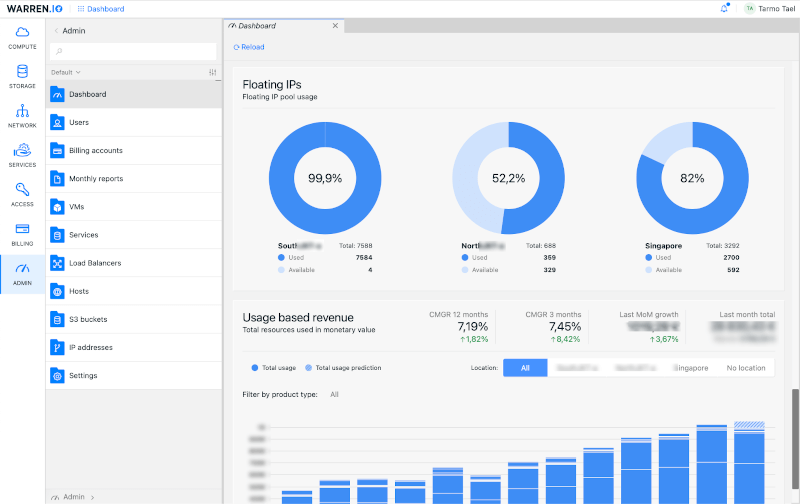
2. Warren.io
Warren is a platform that provides cloud and hosting providers with a self-service solution. The platform is managed by the Warren team, which frees up the provider’s team to focus on core business activities.
Warren is updated twice a month, ensuring that providers always have the latest version and never experience downtime or service disruptions.
Warren offers a number of competitive advantages, including:
- Reliability and High Availability – Warren is designed to be reliable and highly available, with a multi-cluster architecture and a distributed storage system, which means that applications will be up and running even if there are hardware failures or network outages.
- Scalability – Warren is a scalable platform that allows providers to easily add or remove resources as needed. This makes it a great choice for businesses that are growing or that need to be able to handle spikes in demand.
- Cost-Effectiveness – Its cost-effective revenue-sharing business model motivates partners with no upfront costs, low ongoing costs, and shared risk.
- Easy to Use – It is easy to use, with a user-friendly interface that makes it easy to manage day-to-day operations.
- Hourly Resource Usage Metering – Its hourly resource usage metering allows providers to track their costs and optimize their usage.
- Supporting Local Payment Gateways – Its global payment capabilities make it easy for providers to accept payments from customers around the world.
- Admin and Operational Features _ It provides a suite of tools and features to help providers manage their cloud infrastructure, including abuser management, support, onboarding automation, and payment resolution.
Warren is a reliable, scalable, and cost-effective cloud and hosting platform that can help you grow your business.
3. VMware vSphere
VMware vSphere is the world’s leading server virtualization platform for building cloud infrastructure. With tons of different powerful features, vSphere is a truly state-of-the-art software virtual machine management software. It is an ideal solution for large VPS providers with appropriate budgets and professional staff.
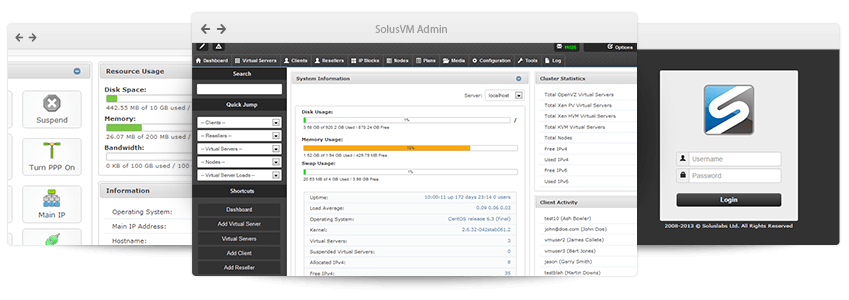
4. SolusVM – Solus Virtual Manager
Solus Virtual Manager (SolusVM) is a commercial VPS management solution. It provides full support of OpenVZ, Linux KVM, Xen Paravirtualization, and XEN HVM. SolusVM-friendly GUI allows users to manage VPS clusters.
5. oVirt
oVirt is an open-source distributed virtualization management solution created by the Red Hat community, that allows you to manage your complete enterprise infrastructure from an easy-to-use web-based front-end with platform-independent access.
oVirt uses the trusted KVM hypervisor and is developed upon various other community projects, including libvirt, Gluster, PatternFly, and Ansible.
6. Proxmox Virtual Environment
Proxmox Virtual Environment is an easy-to-use open-source virtualization platform for running Virtual Appliances and Virtual Machines. The software itself is free, but support services (even access to Community Forum) are provided on a paid basis per month.
7. Virtkick
Virtkick is a commercial “all-in-one” tool, which combines billing software and VPS management tools. The GUI is minimalistic and easy to use even for VPS clients. Virtkick developers promote this solution to be a perfect tool for small data centers or game hosting services.
8. Virtualizor – VPS Control Panel
Virtualizor is a commercial VPS Control Panel from Softaculous developers. It supports OVZ, KVM, and Xen: PV/HVM/Server virtualizations. VPS administrators and average users can easily manage their virtual machines using this software product.
9. Xen Orchestra
Xen Orchestra is a commercial web UI, which provides an intuitive, powerful, and completely web-based interface specially designed to manage XenServer (or Xen+XAPI) infrastructure (VM, servers, pools, etc.)
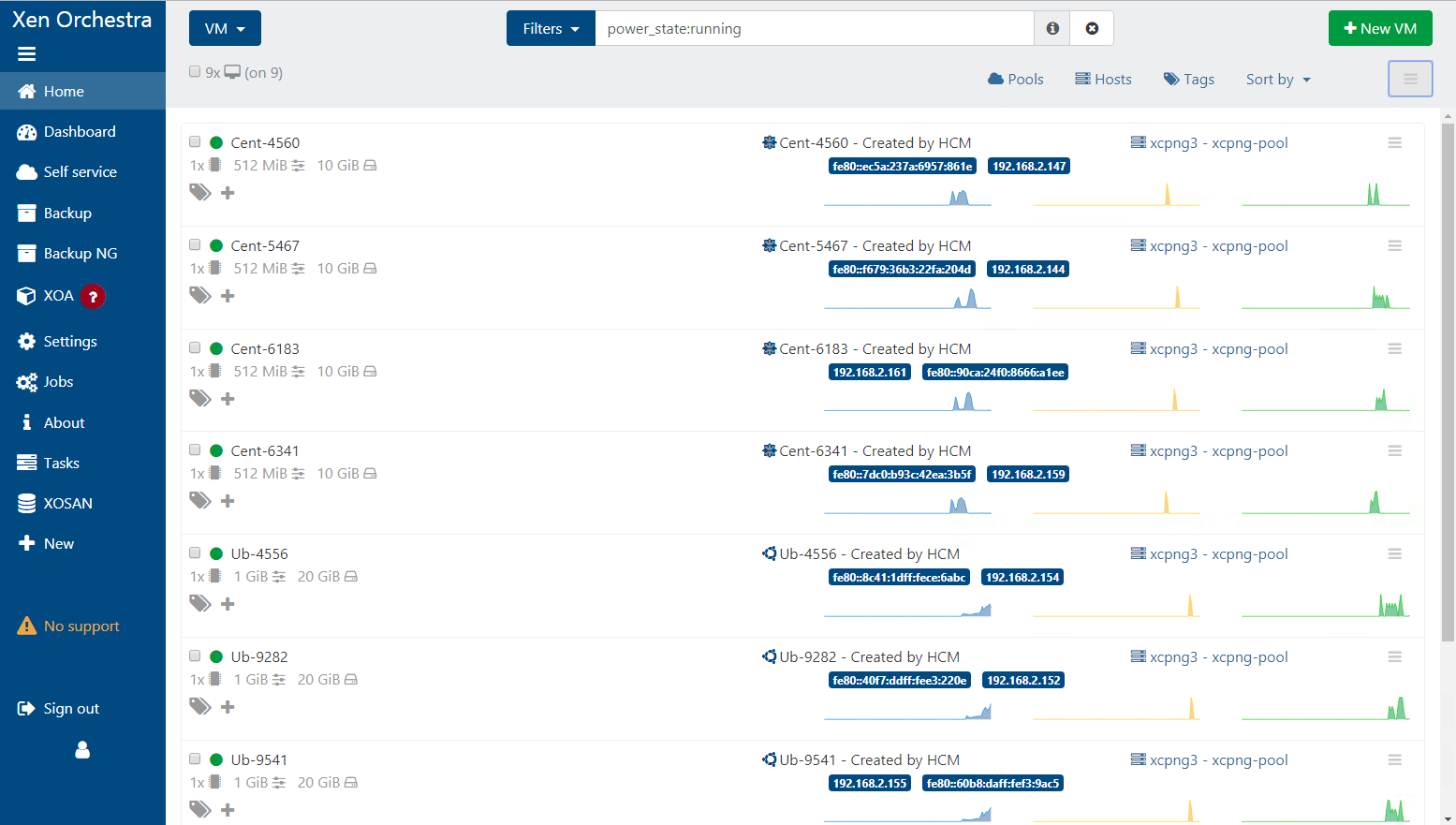
For more information on how to install XenServer with the Xen Orchestra web interface, read our articles:
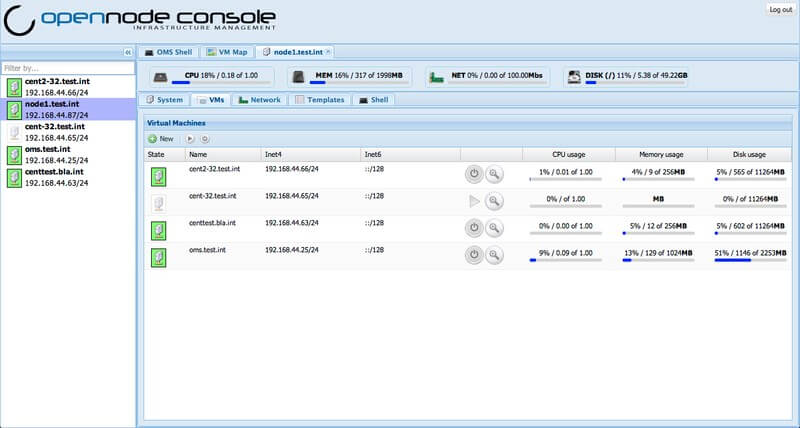
10. OpenNode Cloud Platform
OpenNode Cloud Platform is an open-source server virtualization and management solution, specially designed for government organizations. It offers an easy and flexible way of creating a private or hybrid cloud for public sector services.
We made an overview of the 10 most popular control panels with web interfaces for virtual machine management. We hope that our article helped you choose the best solution according to your specific needs, and made your business grow.



archipel redirects to spyware domain.
@Jerzy,
It seems Archipel is dead…
Even tough this is from 2016 theres a lot wrong with the list some of the commercial solutions are a joke beside it should be 2 articles.
one for cloud solutions (multiple server, central storage, virtual routers and stuff) and another the simple version
mainly one or just a few server mainly web frontend for libvirt.
on this note webvirtmanager is not developed in years which follows it footstepts (even tough i am not a fan of its limitations)
Hi Nikita Nesmiyanov ,
Thanks for sharing, I have learned a lot of CP in your post. But I think you also can check another control panel that calls aapanel.
Fan
really oVirt is missing from that list?!?!!
You forgot openxenmanager
Hello,
I would like to share also our Private Cloud management system, it allows to automatically create virtual machines with an easy-to-use Web Interface. If you want to know more please check cloud-bricks docs
Thanks a lot for this space!
Miguel
Nikita, I want to use to create virtual machine, Linux like RHEL, CentOS and some Windows Server.
I want to create it, because I intend study and practice. I have my desktop with Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and my laptop with linux mint. Through the linux mint on laptop I can control and manager my virtual machines or I can use them by own host.
Roberson, if you want to create one virtual machine for every OS (RHEL, CentOS and Windows Server), I think, you should use the command line to deploy VMs ’cause you’ll earn much more practice on manual deployment. Those panels that mentioned above are for situation when you need to deploy at least 50 VMs per day or when you need to automate VM sales.
In your situation, to earn skills and practice, install libvirt (KVM) or openvz package on your desktop and then create/modify/delete VMs from your laptop via SSH. I think, it’s the best way for your purposes.
Oh, by the way: usually, control panels install libvirt or openvz automatically.
Thanks a lot Nikita for your support.
I have installed the libvirt (KVM) in my desktop.
Roberson, if you want to create one virtual machines for every OS (RHEL, CentOS and Windows Server), I think, you should use the command line to deploy VMs ’cause you’ll earn much more practice on manual deployment. Those panels that mentioned above are for situation when you need to deploy at least 50 VMs per day or when you need to automate VM sales.
In your situation, to earn skills and practice, install libvirt (KVM) or openvz package on your desktop and then create/modify/delete VMs from your laptop via SSH. I think, it’s the best way for your purposes.
Oh, by the way: usually, control panels install libvirt or openvz automatically.
How are you Nikita.
First of all, thank you for sharing with us your knownledgement. I wanna ask you, which tools of that mentioned aboveit’s the better for my use. Solus ? I going to install KVM following this guide https://www.tecmint.com/install-and-configure-kvm-in-linux/
And, i’d like to know, which tools that you told above, is better. I can install this tools in the host that has the KVM or whenever ?
Thanks
Hi, Roberson.
Could you please share some details on what do you want to use the virtualization for? Depending on your answer I can give you a helpful comment.