In an unfortunate event of forgetting or losing your MySQL root password, you will surely need a way to recover it somehow. What we need to know is that the password is stored in the users table. This means that we need to figure out a way to bypass the MySQL authentication, so we can update the password record.
Luckily there is an easy to achieve and this tutorial will guide you through the process of recovering or resetting root password in MySQL 8.0 version.
As per MySQL documentation there are two ways to reset the root MySQL password. We will review both.
Reset MySQL Root Password Using –init-file
One of the ways to reset the root password is to create a local file and then start the MySQL service using --init-file option as shown.
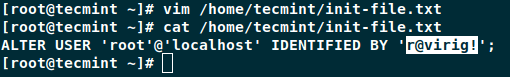
# vim /home/user/init-file.txt
It is important that you make sure that file is readable by the mysql user. Within that file paste the following:
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'new_password';
In the above change “new_password” with the password that you wish to use.
Now make sure that the MySQL service is stopped. You can do the following:
# systemctl stop mysqld.service # for distros using systemd # /etc/init.d/mysqld stop # for distros using init
Then run the following:
# mysqld --user=mysql --init-file=/home/user/init-file.txt --console
This will start the MySQL service and during the process it will execute the init-file that you have created and thus the password for the root user will be updated. Make sure to delete the file once the password has been reset.

Make sure to stop the server and start it normally after that.
# systemctl stop mysqld.service # for distros using systemd # systemctl restart mysqld.service # for distros using systemd # /etc/init.d/mysqld stop # for distros using init # /etc/init.d/mysqld restart # for distros using init
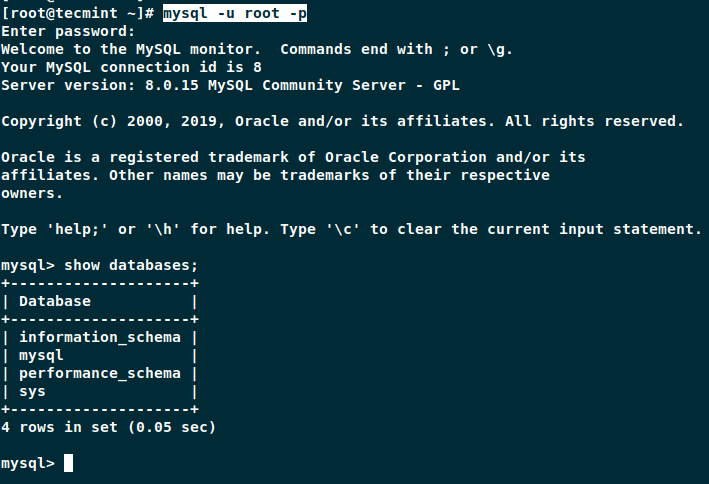
You should now be able to connect to the MySQL server as root using the new password.
# mysql -u root -p
Reset MySQL Root Password Using –skip-grant-tables
The second option we have is to start the MySQL service with the --skip-grant-tables option. This is less secure as while the service is started that way, all users can connect without password.
If the server is started --skip-grant-tables, the option for --skip-networking is automatically activated so remote connections will not be available.
First make sure that the MySQL service is stopped.
# systemctl stop mysqld.service # for distros using systemd # /etc/init.d/mysqld stop # for distros using init
Then start the service with the following option.
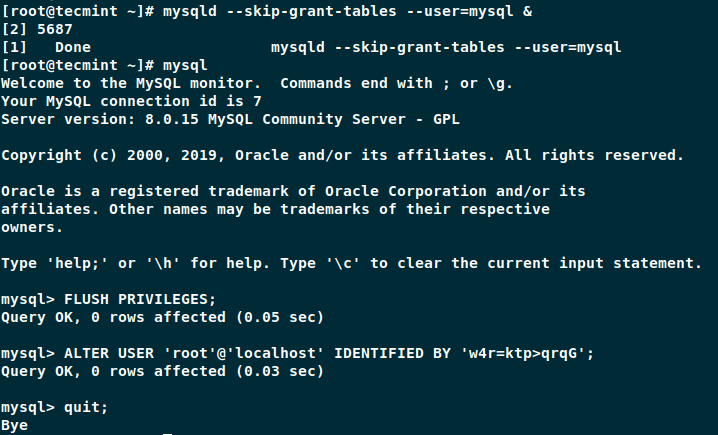
# mysqld --skip-grant-tables --user=mysql &
Then, you can connect to the mysql server by simply running.
# mysql
Since account-management is disabled when the service is started with --skip-grant-tables option, we will have to reload the grants. That way we will be able to change the password later:
# FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Now you can run the following query to update the password. Make sure to change “new_password” with the actual password you wish to use.
# ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'new_passowrd';
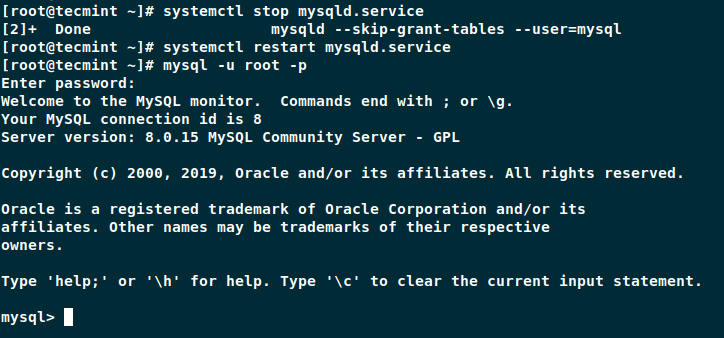
Now stop the MySQL server and start it normally.
# systemctl stop mysqld.service # for distros using systemd # systemctl restart mysqld.service # for distros using systemd # /etc/init.d/mysqld stop # for distros using init # /etc/init.d/mysqld restart # for distros using init
You should be able to connect with your new password.
# mysql -u root -p
You might also like to read these useful following MySQL related articles.
- How to Install MySQL 8 in CentOS, RHEL and Fedora
- 15 Useful MySQL Performance Tuning and Optimization Tips
- 12 MySQL Security Practices for Linux
- 4 Useful Commandline Tools to Monitor MySQL Performance
- MySQL Database Administartion Commands
Conclusion
In this article you learned how to reset lost root password for the MySQL 8.0 server. I hope the process was easy.





THANKS!!! Your instructions worked great!
ERROR 2002 (HY000): Can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket ‘/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock’ (2)
Use this article to solve ERROR 2002 (HY000) error – Useful Tips to Troubleshoot Common Errors in MySQL
The first method, using an init file, totally failed for me. I couldn’t restart mysql after that. I was able to get the
--skip-grant-tablemethod to work, however, I had to manually kill the mysqld process. systemctl stop mysqld would not stop it.Thanks! Perfect. Just one caveat: “Sudo” did not seem to work well. Better to “sudo su – root” and be fully root.
I followed both the methods.
1. reset password through init file.
2.
--skipgrant table option.But I stuck with both the methods. These methods did not work for me. As I tried to login to mysql database, showing error again.
If you required snapshots, will share.