Netstat – derived from the words network and statistics – is a command-line utility used by system administrators for analyzing network statistics.
It displays a whole manner of statistics such as open ports and corresponding addresses on the host system, routing table, and masquerade connections.
In this article, we will walk you through how you can install the netstat command in different Linux distributions.
How to Install netstat Command in Linux
The package that contains netstat is called net-tools. On modern systems, the netstat utility comes pre-installed and there’s no need to install it.
On older systems, however, you are likely to bump into an error when you run the netstat command.
bash: netstat: command not found
Therefore, to install netstat on Linux distributions, run the command.
$ sudo apt install net-tools [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install net-tools [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/net-tools [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add net-tools [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S net-tools [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install net-tools [On OpenSUSE]
Once installed, run the command below to check the version of netstat installed.
# netstat -v
How to Use netstat Command in Linux
You can invoke the netstat command on any of the Linux distributions to get different statistics on your network.
1. Viewing the Network Routing Table
You use the -r flag to show the network routing table to get something similar to the output below.
# netstat -nr
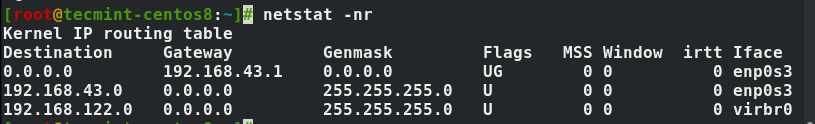
The -n option forces netstat to print addresses separated by dots instead of using symbolic network names. The option is useful for avoiding address lookups over a network.
2. Display Network Interface Statistics
Use the -i flag to get an output of statistics of a network interface that is configured. The -a option prints all present interfaces in the kernel.
# netstat -ai

3. Show Network Connections
The netstat command utility supports options that display active or passive sockets using the options -t, -n, and -a. The flags show RAW, UDP, TCP, or UNIX connection sockets. Adding the -a option, it will sow sockets ready for connection.
# netstat -ant
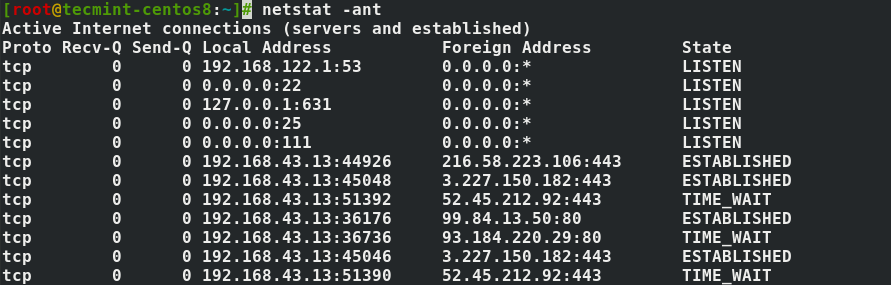
4. Show Network Services
To list services, their current state, and their corresponding ports, run the command.
# netstat -pnltu
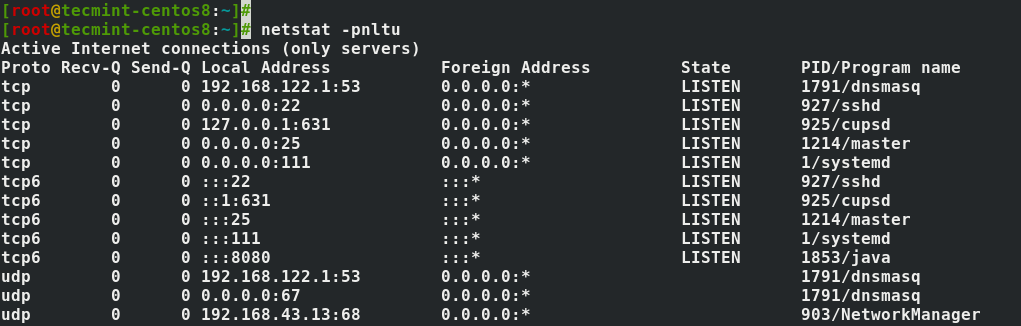
In this article, we shed light on how you can install the netstat command and how it is used to check a wide array of network statistics.
It’s also important to point out that netstat has been deprecated and instead, ss utility has taken its place in displaying more refined network statistics.





For SUSE 15 to install netstat:
I should point out that it is actually the most modern system that is likely to be missing netstat since ss is a newer replacement.
Arch Linux install is incorrect. “netstat-nat” is a different package that does not install the same.
It should be:
Thank you for providing the proper instructions for installing the net-tools package on Arch Linux.