You must have probably installed Fedora 24 server edition on your machine and you are eager and looking forward to setting up a web server to run websites and web applications. Look no further, because we shall do all that here, with simple and easy steps that you will appreciate at the end.

In this how to guide, we shall run through the different steps of how you can install LEMP stack on your Fedora 24 web server. Similar to LAMP, but under LEMP, we use Nginx web server.
Don’t Miss: Install LAMP (Linux, Apache, MariaDB and PHP) on Fedora 24 Server
Step 1: Updating System Packages
You can get started by updating your system packages as follows:
# dnf update
When that is done, proceed to install the composite LEMP packages.
Step 2: Install Nginx Web Server
Nginx is an alternative to Apache web server, it is light weight and consumes less system resource hence its high performance, stability and flexibility in enterprise productions environments.
To install Nginx on Fedora 24, issue the command below:
# dnf install nginx
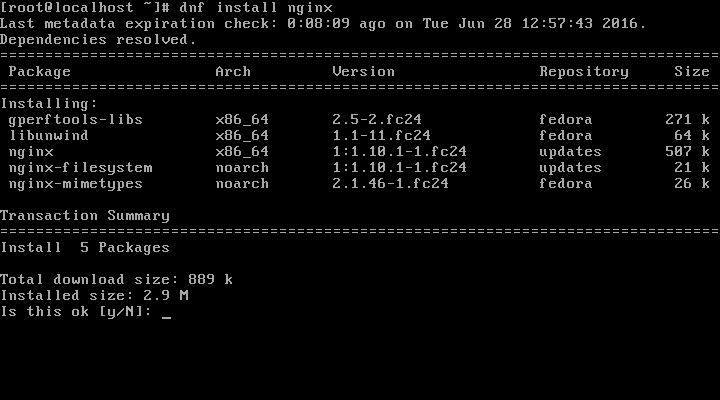
Once the installation is complete, you need to manage the Nginx service on your system. First you need to set it to start automatically at boot time by running the command below:
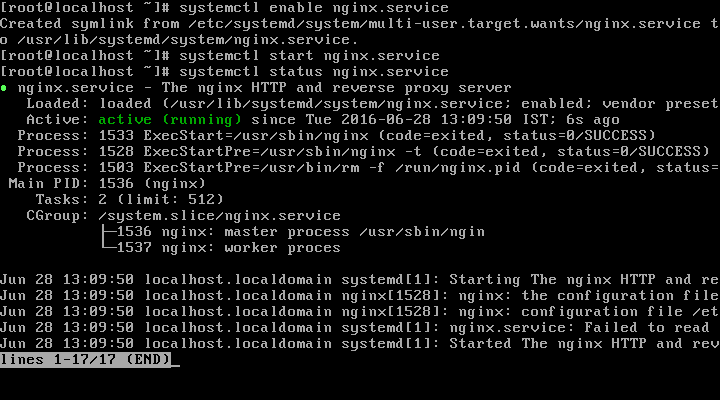
# systemctl enable nginx.service
Then start the service as follows:
# systemctl start nginx.service
Next, check to see that Nginx server is running, you can issue the command below to do that:
# systemctl status nginx.service
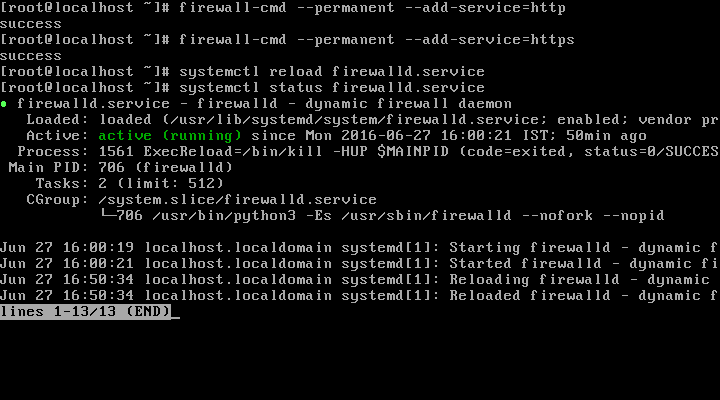
In order to view your Nginx web server over HTTP/HTTPS protocol, you need to allow access to it through the system firewall. To do so, run the following commands:
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http # firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
Then reload the system firewall configurations to effect the above changes as follows:
# systemctl reload firewalld
Now move on to set your Nginx server_name directive, using your favorite editor, open the file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf and find the configuration directive as shown:
server_name server-ip-address;
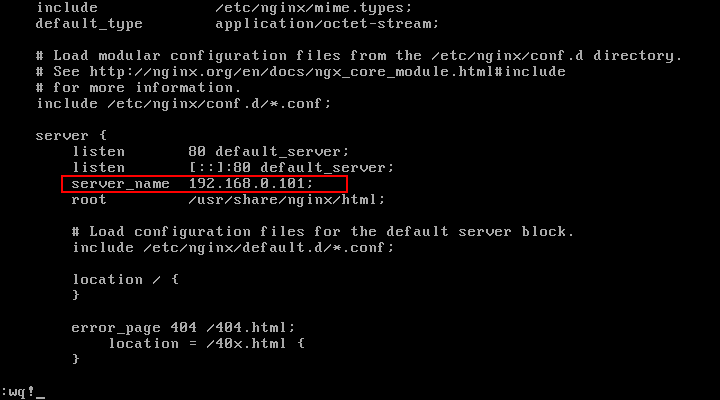
Note: The Nginx document directory root is /usr/share/nginx/html, and this is where you can place all your web files.
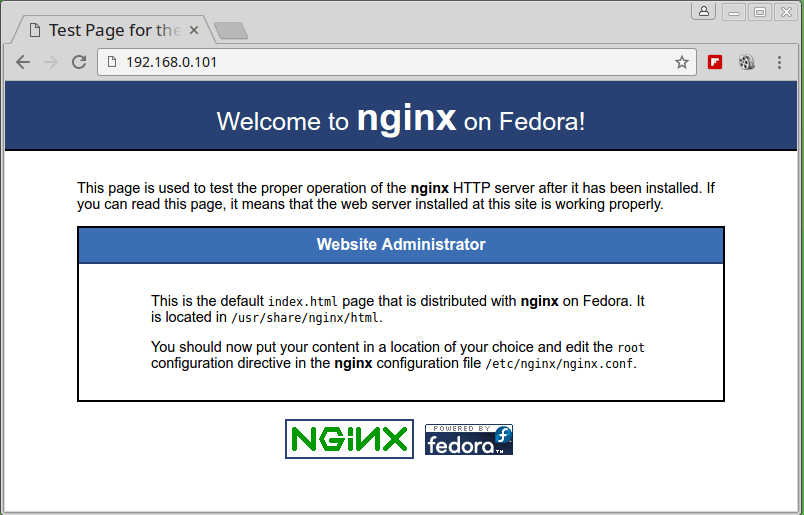
One more important thing to do under Nginx installation is to check whether the Nginx installation index page can load in your web browser, therefore open your web browser and enter the URL:
http://server-ip-address
You should be able to view this page below:
Step 3: Install MariaDB Server
MariaDB is a fork of the most famous MySQL relational database server, to install MariaDB on Fedora 24 server, issue the command below:
# dnf install mariadb-server
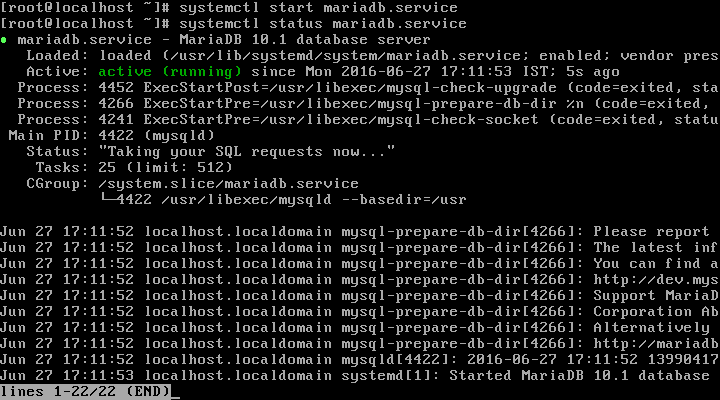
After completing the MariaDB installation, you need to enable, start and verify the service by running following series of commands.
# systemctl enable mariadb-service # systemctl start mariadb-service # systemctl status mariadb-service
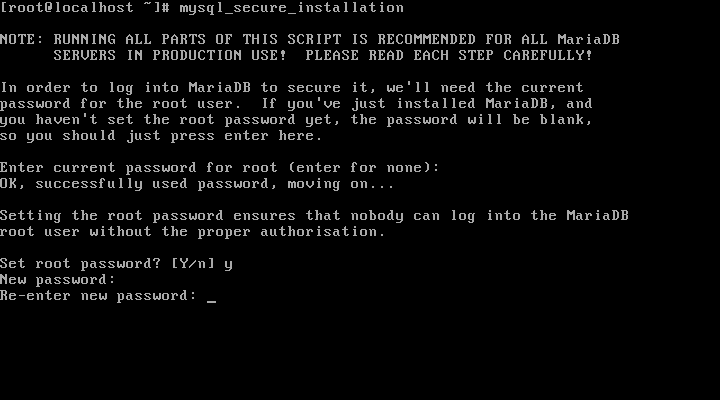
Now it’s time to secure your MariaDB installation using following command:
# mysql_secure_installation
After executing above command, you will be asked a few questions as follows:
Enter current password for root(enter for none): Here, Simply press [Enter] Next you will be asked to set a root user password for your MariaDB server. Set root password? [Y/n]: y and hit [Enter] New password: Enter a new password for root user Re-enter new password: Re-enter the above password Remove anonymous users? [Y/n]: y to remove anonymous users It is not always good to keep your system open to remote access by root user, in case an attacker lands on your root user password, he/she can cause damage to your system. Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n]: y to prevent remote access for root user. Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n]: y to remove the test database Finally, you need to reload privileges tables on your database server for the above changes to take effect. Reload privileges tables now? [Y/n]: y to reload privileges tables
Step 4: Install PHP and Modules
To install PHP on Fedora 24 along with its modules, use the command below:
# dnf install php php-commom php-fpm php-mysql php-gd
Now that PHP and some PHP modules have completed installing, you need to configure PHP so that you can run PHP files.
By default, PHP-FPM is configured to be used with Apache web server, but for our case here, we are using Nginx web server. Therefore we need to change that setting in the steps below:
Using your favorite editor, open the file /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf as follows:
# vi /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
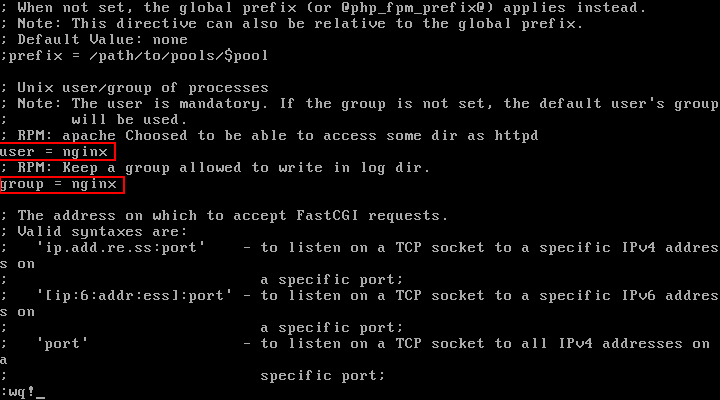
Then change the values of user and group from apache to nginx in the following lines:
; RPM: apache Choosed to be able to access some dir as httpd user = nginx ; RPM: Keep a group allowed to write in log dir. group = nginx
Then restart PHP-FPM and Nginx web server to effect the changes above:
# systemctl restart php-fpm.services # systemctl restart nginx.services
After that, confirm that they are running be issuing the commands below:
# systemctl status php-fpm.services # systemctl status nginx.services
Now you can test it all, using your favorite editor, create a file called info.php in your Nginx root directory as follows:
# vi /usr/share/nginx/html/info.php
Add the following lines in the file, save it and exit.
<?php phpinfo() ?>
Then open your web browser and enter the following URL to verify the PHP information:
http://server-ip-address/info.php

At this point, you must have successfully installed and configured LEMP stack on your Fedora 24 server. In a few cases, some of you must have encountered errors or want more explanation concerning an issue of concern, you can leave a comment in the comment section below and we shall find solutions together.






Hi,
really nice info but it’s not include how to link the Nginx with php-fpm and which configuration I need to do to get the service work probably as you knew the php-fpm is work as independent service
@Mozuffer Mohamed Hago
Sorry about that, here i only pointed out setting PHP FPM to work with Nginx instead of Apache2
Here is a detailed guide from the Nginx website that explains how to connect Nginx with PHP FPM:
https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/examples/phpfcgi/#
What if you want to use /home/username/www ?
@kimmono,
You mean Apache document root path? if yes, you can replace
/var/www/htmlwith/home/username/wwwinhttpd.conffile.