R is a popular programming language and software environment used to build statistical and graphical computing tools for data science. It is in many ways similar to the S programming language and environment; R is a different implementation of S. Although there are some significant differences between the two.
R is free software available under the terms of the Free Software Foundation’s GNU General Public License. It is also cross-platform, it can be compiled and run on Linux, and other UNIX-based operating systems including FreeBSD and MacOS; and Windows as well.
R supports a variety of statistical (linear and nonlinear modeling, classical statistical tests, time-series analysis, classification, clustering, etc) and graphical techniques.
Table of Contents
R Programming Language’s Key Features
- Offers effective data handling and storage facility.
- Provides a suite of operators for calculations on arrays, in particular matrices.
- Ships with a large, coherent, integrated collection of intermediate tools for data analysis.
- Offers graphical facilities for data analysis and display either on-screen or on hardcopy.
- Provides conditionals, loops, user-defined recursive functions, and input and output facilities.
- Allows users to add additional functionality by defining new functions.
- It’s highly extensible via packages, about eight packages are supplied with the R distribution and many others are available through the CRAN (Comprehensive R Archive Network) family of Internet sites.
- Supports for easily creating well-designed publication-quality plots such as mathematical symbols and formulae where needed, and.
- Most S programs can run unaltered in R.
- Also, for computationally-intensive tasks, C, C++, and Fortran code can be linked and called at run time.
- Ships with comprehensive documentation, in LaTeX-like documentation format.
Installing R Programming Language in Linux
You can install R programming language packages on your Linux system as shown below. On RHEL-based distributions, you need to it from the EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository.
Note: Remember to run the correct set of commands for your Linux distribution.
Install R on Ubuntu
$ sudo apt update -qq $ sudo apt install --no-install-recommends software-properties-common dirmngr $ wget -qO- https://cloud.r-project.org/bin/linux/ubuntu/marutter_pubkey.asc | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/cran_ubuntu_key.asc $ sudo add-apt-repository "deb https://cloud.r-project.org/bin/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs)-cran40/" $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install --no-install-recommends r-base
Install R on Debian
$ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-key '95C0FAF38DB3CCAD0C080A7BDC78B2DDEABC47B7' $ sudo add-apt-repository "deb https://cloud.r-project.org/bin/linux/debian $(lsb_release -cs)-cran40/" $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install --no-install-recommends r-base
Install R on Fedora
$ sudo dnf install R
Install R on RHEL Systems
--------- On RHEL 9 ---------
$ sudo subscription-manager repos --enable codeready-builder-for-rhel-9-$(arch)-rpms
$ sudo dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm
$ sudo dnf install R
--------- On RHEL 8 ---------
$ sudo subscription-manager repos --enable codeready-builder-for-rhel-8-$(arch)-rpms
$ sudo dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm
$ sudo dnf install R
--------- On RHEL 7 ---------
$sudo subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-*-optional-rpms \
--enable rhel-*-extras-rpms \
--enable rhel-ha-for-rhel-*-server-rpms
$ sudo yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
$ sudo dnf install R
Install R on CentOS Stream
--------- On CentOS Stream 9 --------- $ sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled crb $ sudo dnf install epel-release epel-next-release $ sudo dnf install R --------- On CentOS Stream 8 --------- $ sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertools $ sudo dnf install epel-release epel-next-release $ sudo dnf install R --------- On CentOS 7 --------- $ sudo yum install epel-release $ sudo dnf install R
Install R on Rocky and AlmaLinux
--------- On Rocky and AlmaLinux 9 --------- $ sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled crb $ sudo dnf install epel-release $ sudo dnf install R --------- On Rocky and AlmaLinux 8 --------- $ sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertools $ sudo dnf install epel-release $ sudo dnf install R
Install R on openSUSE
$ sudo VERSION=$(grep "^PRETTY_NAME" /etc/os-release | tr " " "_" | sed -e 's/PRETTY_NAME=//' | sed -e 's/"//g') $ sudo zypper addrepo -f http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/devel\:/languages\:/R\:/patched/$VERSION/ R-base $ sudo zypper install R-base R-base-devel
Verify R Installation in Linux
After installing the R packages, you can verify if the environment is set up well. To start the R program, run the R command which will launch the R program shell as shown in the next screenshot.
$ R
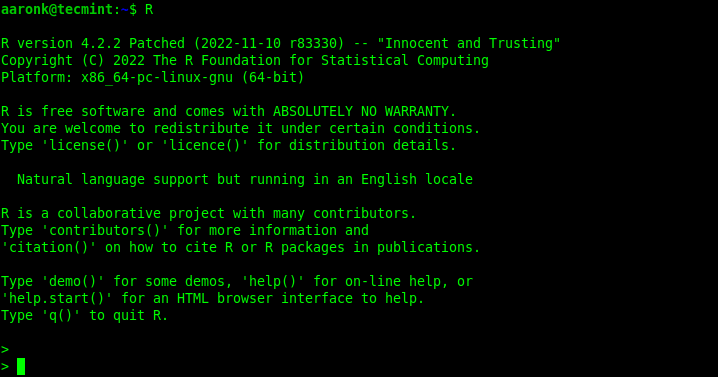
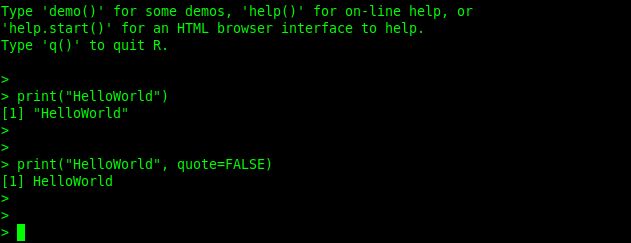
You can run a hello world program in R as shown:
>print("HelloWorld")
>print("HelloWorld", quote=FALSE)
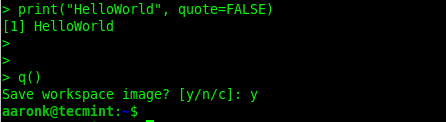
To quit the R program shell, issue the q() command. You will be prompted whether you want to save the data from your R session, enter y for yes or n for no, or c to cancel:
> q()
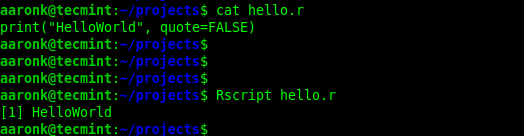
Besides, you can run an R script using the Rscript (front end for scripting with R) command as follows:
$ cat hello.r $ Rscript hello.r
For more usage options, read the R and Rscript man pages:
$ man R $ man Rscript
We have come to the end of this guide. For more information, visit the R project’s official website.





I installed R on AlmaLinux 9 following the instructions in this article. However, when I try to start R, it fails with the following error message:
System Information:
@Gosta,
The error message you’re seeing, specifically
GFORTRAN_8not found, indicates that the installed version of libgfortran does not meet the requirements for FlexiBLAS, which is likely a dependency for R. FlexiBLAS is trying to use a version of libgfortran that isn’t installed on your AlmaLinux 9 system.Here’s a step-by-step approach to troubleshoot and resolve this issue:
1. First, make sure all your system packages are up to date. Sometimes updating can solve compatibility issues.
2. Next, you might need to install the GCC version that includes the correct libgfortran library.
3. Download and install a compatible libgfortran version.
4. If you continue to experience issues with FlexiBLAS, you might want to configure it to use a different BLAS library that doesn’t have the same version dependency.
5. After completing the above steps, try running R again to see if the error is resolved:
6. If issues persist, you might consider reinstalling FlexiBLAS or R, as an incorrect installation can sometimes cause these issues.
After completing these steps, R should start without the FlexiBLAS error. Let me know if you run into further issues!
@Ravi Saive
Thank you so much for your help!
I went through it step by step, but
Rstill isn’t working.I think the main issue now is with step 3, the second line:
sudo dnf install compat-gcc-8-gfortran.It gives the following error:
No error messages occurred with any of the other steps, but R still aborts with the message:
@Gosta,
It looks like the issue is with the version of
libgfortranrequired byflexiblas. Sincecompat-gcc-8-gfortranisn’t available in your current repository, you can try the following steps to resolve the issue:Install the correct version of
libgfortran:Next, ensure that the correct version of
flexiblasis installed:Make sure that your system is up-to-date and has all the necessary dependencies:
Once you’ve done this, try running
Ragain.Hopefully, this resolves the error. Let me know how it goes!
@Ravi Saive
R is running properly now :-)
I went through your steps. They all gave back: “Nothing to do”.
So I guess the quite big number of system updates that occurred during the last few days rather did the thing.
Nevertheless, I really appreciate your help.